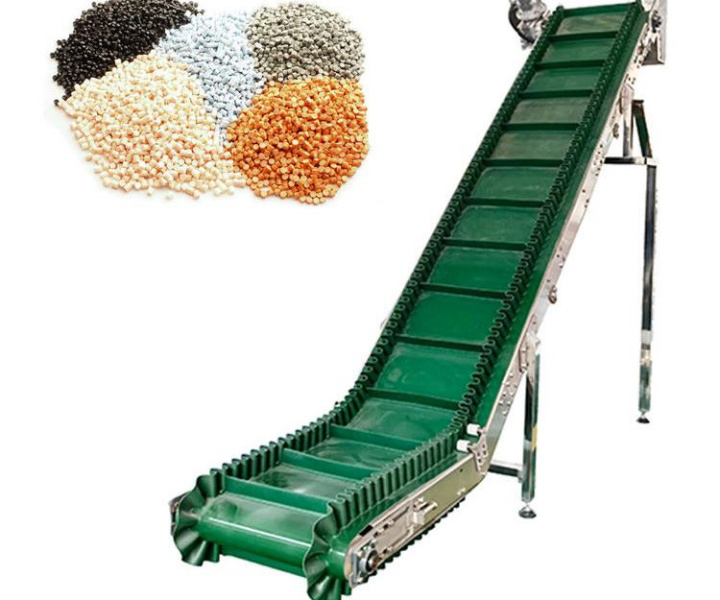
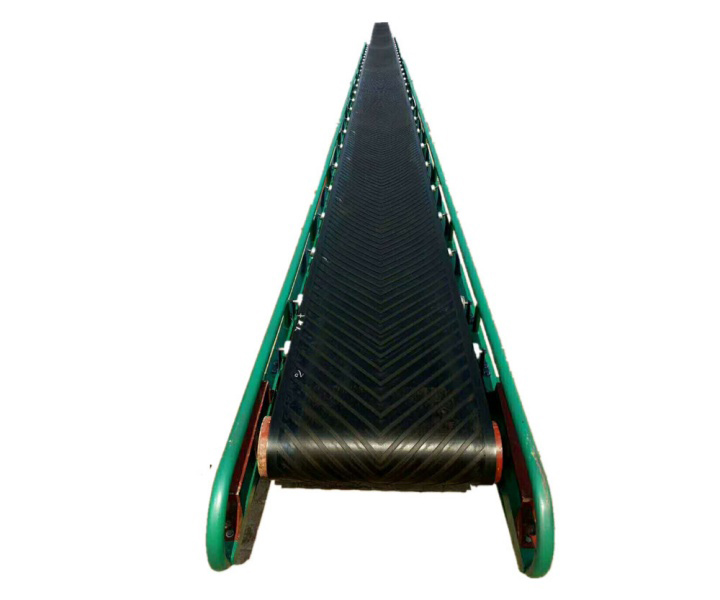









Usually used to transport and stack fertilizer raw materials or finished products quickly and efficiently during the fertilizer production process.
![]()
![]()
Price::$499.00-$6,000.00/Set
Consult now and enjoy a 10% discount
Conveying capacity: 30-3000m³/h
Conveying speed: 1.25-2.0m/s
Conveying length: 10 meters
Conveying Angle: 0°-90°
Belt width: 400-2400mm
Frame Material: Carbon Steel/Stainless Steel
Application: It is suitable for fertilizer production plants, farms and other places and can transport various fertilizer raw materials and finished products, including granular fertilizers, powdered fertilizers, organic fertilizers, etc.
Commitment:Free Shipping/5 Days Delivery/30-Day Returns/Support Customization
Fertilizer belt conveyor is a type of conveyor system specifically designed for the transportation and handling of fertilizers or fertilizer-related products. It is a specialized conveyor system used in agricultural and industrial settings to efficiently move fertilizers from one location to another. The equipment usually consists of a conveyor belt, a drive device, a supporting structure, etc., and can transport fertilizer in a horizontal, inclined or vertical direction.

Fertilizer belt conveyors are designed to handle various types of fertilizers, including granular fertilizers, powdered fertilizers, and blended fertilizers. Fertilizer belt conveyors have the characteristics of wear resistance and corrosion resistance, they are widely used in agricultural operations, fertilizer production facilities, distribution centers, and other settings where efficient and reliable fertilizer transportation is required.
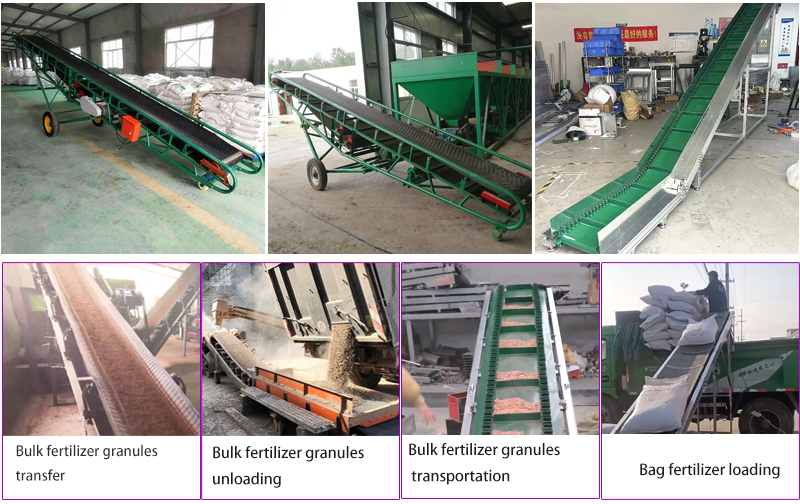


Fertilizer belt conveyors are used in all stages of the fertilizer production and distribution process. Here are some common applications for fertilizer belt conveyors:
Raw material handling: Used to transport raw materials such as mined minerals, organics or chemical components to processing or blending areas. This could include materials such as phosphate rock, potash, urea, ammonium nitrate and other ingredients used in fertilizer production.
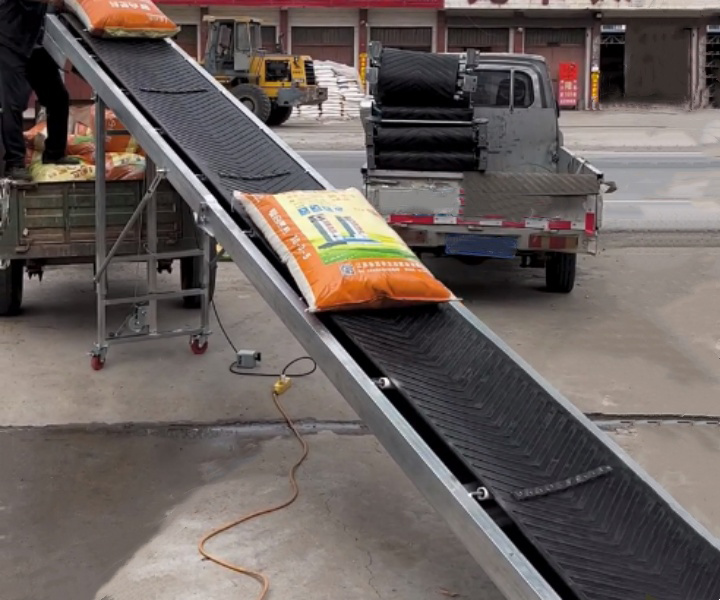
Packing and Bagging: The finished fertilizer is transported from the production line to the packing area, where it is weighed, bagged and prepared for distribution.
Warehouse and Distribution: Used to efficiently move pallets or bulk fertilizer bags between storage areas, loading docks and trucks. They help simplify logistics and distribution processes.
Retail and Agricultural Supply: Used in retail stores, garden centers, and agricultural supply stores to dispose of bagged fertilizers. They assist in the transfer of luggage from the storage area to the point of sale or customer pickup location.
Fertilizing equipment: Belt conveyors can be integrated into fertilizing equipment, such as fertilizer spreaders or seed drills. They transport bulk fertilizer from hoppers or storage bins to distribution agencies, ensuring consistency and accuracy in field application.
Fertilizer belt conveyors can be divided into the following types according to different classification standards:
| Types | Mobile Fertilizer Belt Conveyor | Inclined Fertilizer Belt Conveyor | Trough Fertilizer Belt Conveyor |
| Pictures |  |
 |
 |
| Features | It is mobile and flexible, can be freely moved and arranged according to the needs of the production site, and is suitable for places where the conveying position needs to be changed frequently. | It is designed to convey fertilizer at an inclined angle and is suitable for places that need to cross height differences, such as conveying from the ground to storage facilities. | With trough conveyor belt, can prevent fertilizer from overflowing, suitable for the conveying of granular fertilizer or granular fertilizer,ensuring that fertilizer will not be scattered or accumulated during conveying process. |
Efficient and reliable transportation
It can process a large amount of fertilizer continuously, ensuring the whole process is smooth and consistent. This increases productivity and reduces downtime.
Increased productivity
The belt automates and simplifies fertilizer transportation without manual handling or reliance on slower transportation methods. Increased efficiency can increase productivity and reduce labor requirements.
Accurate and Controlled Feeding
Capable of accurately and controlled feeding of fertilizers into various processes such as blending, blending, pelletizing or packaging. The steady and controlled flow of fertilizer ensures the precise composition and quality of the final product.
Dust control
Fertilizers will generate dust during handling and transportation, which may cause health and safety problems. Belt conveyors can be equipped with dust containment systems such as enclosures, hoods or dust collection devices to minimize the release of dust particles into the surrounding environment.
| Belt width (mm) |
Conveying length(m) Power(kw) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Conveying amount (t/h) |
||
| B400 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 30-60 |
| 3 | 3-4 | 4-7.5 | |||
| B500 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 40-80 |
| 3 | 4-5.5 | 5.5-7.5 | |||
| B650 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 80-120 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-11 | |||
| B800 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 120-200 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-15 | |||
| B1000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 200-320 |
| 5.5 | 7.5-11 | 11-22 | |||
| B1200 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 290-480 |
| 7.5 | 7.5-15 | 15-30 | |||
| B1400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 400-680 |
| 11 | 15-22 | 22-45 | |||
| B1600 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.25-2.0 | 600-1080 |
| 15 | 22-30 | 30-75 | |||
| B1800 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.0-2.0 | 200-1500 |
| 18.5 | 30-45 | 45-110 | |||
| B2000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1000-2000 |
| 22 | 45-55 | 55-132 | |||
| B2400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1500-3000 |
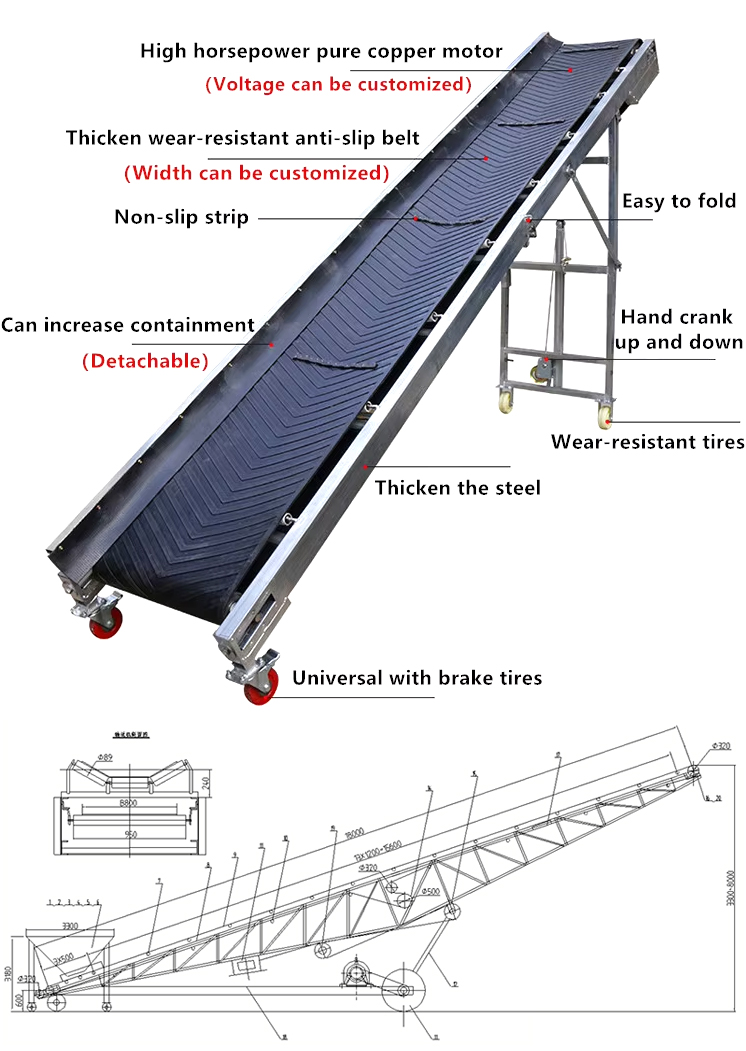
As an important equipment in fertilizer production and transportation, fertilizer belt conveyors often need to be customized to adapt to the layout, material characteristics and process requirements of different production lines. Common customization types are mainly the following:
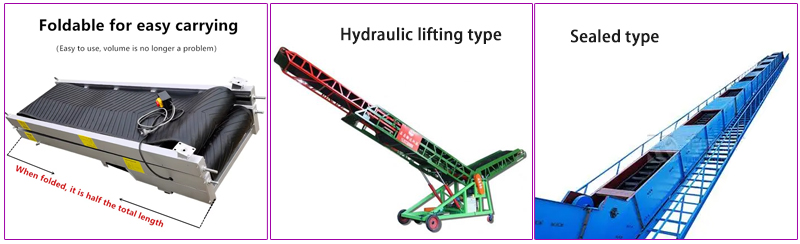
1. Folding type: After folding, it can save a lot of space and is suitable for narrow working conditions. It can be quickly unfolded or folded as needed, which is convenient for adjusting the production line. After folding, it is easy to transport and suitable for mobile operations.
2. Hydraulic lifting type: The height of the conveyor belt is adjusted through the hydraulic system to adapt to the equipment interface at different heights and suitable for material docking between equipment.
3. Sealed type: The closed structure prevents the fertilizer from being contaminated or reduces dust pollution during transportation.
Fertilizer conveyors typically use a variety of belt materials, depending on the specific requirements of the fertilizer being conveyed. Here are some common belt materials used in fertilizer conveyors:

PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC belts are widely used in fertilizer conveyors due to their economy, chemical resistance and durability. They can withstand contact with fertilizers containing acids, alkalis and other chemicals without significant degradation. PVC conveyor belts are also abrasion resistant, moisture resistant and suitable for a wide variety of fertilizer types.
Rubber: Rubber belts are widely used in fertilizer conveyors because of their high tensile strength, elasticity and abrasion resistance. They have good chemical and moisture resistance, which is essential for fertilizer handling. Rubber tapes are available in a variety of compounds, such as natural rubber or synthetic rubber blends, to meet specific application requirements.
Polyurethane (PU): Polyurethane conveyor belts are known for their excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and oils. They have high tensile strength and flexibility for heavy-duty applications and conveying abrasive fertilizers. Polyurethane belts are also resistant to hydrolysis and microbial attack, ensuring long life in wet environments.
Polyester/Nylon (EP/NN): Belts made from a combination of polyester and nylon fibers have high tensile strength and excellent resistance to elongation. They are durable and suitable for conveying heavy duty fertilizers. These belts are typically used on long distance or high capacity fertilizer conveyors.
The choice of belt material depends on factors such as fertilizer type, chemical composition, particle size, temperature and other operating conditions. Always consult your conveyor system manufacturer or belt supplier to select the most suitable belt material for your specific fertilizer conveying application.
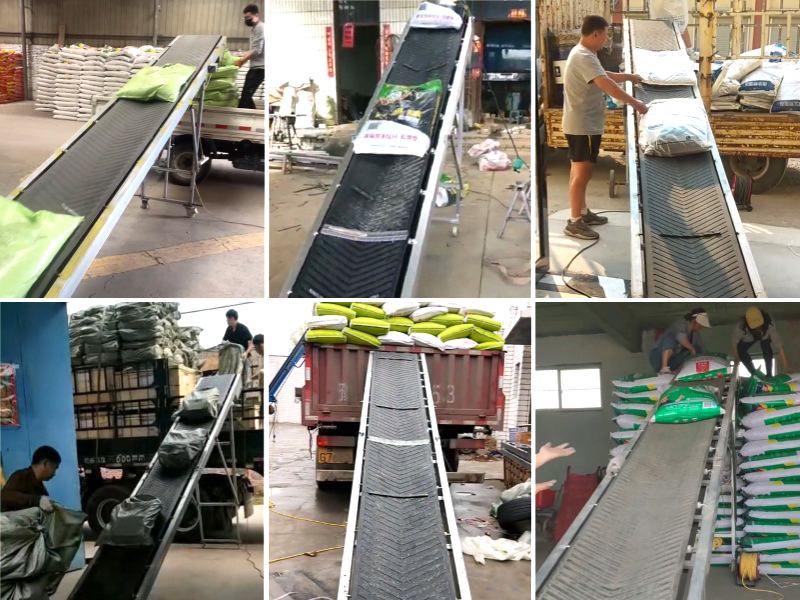

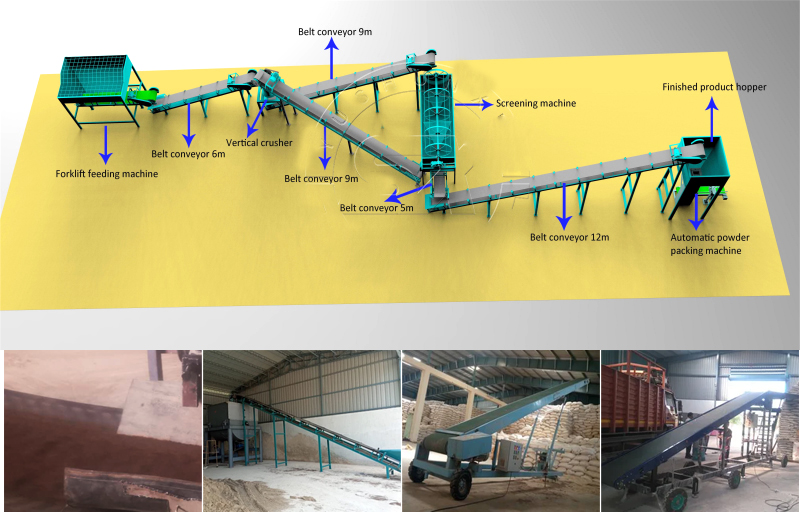
A large fertilizer production company uses fertilizer belt conveyors to transport raw materials such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other fertilizers from storage warehouses to production lines to achieve automated continuous production. The conveyor uses corrosion-resistant materials and professional design to ensure safe fertilizer transportation and product quality. Through automated control and regulation, the conveyor can accurately control the material conveying speed and flow rate, improving the company's production efficiency.

As a professional fertilizer belt conveyor manufacturer, Dahan has many years of technical experience. The manufacturer is committed to producing high-quality and reliable fertilizer conveying equipment. The products produced by the manufacturer cover various models and specifications of belt conveyors to meet the needs of different customers. Xinxiang Dahan pays attention to product quality and technological innovation, and adopts advanced production processes and equipment to ensure the stability and durability of the products. The fertilizer belt conveyors produced are widely used in agriculture, fertilizer plants and other fields, providing customers with efficient and reliable fertilizer conveying solutions.
| Fertilizer types | Applicable belt conveyor types | Reasons for selection |
| Granular fertilizers (such as urea, compound fertilizers) | Ordinary rubber belt conveyor | Granular fertilizers are less abrasive, and ordinary rubber belts can meet the requirements, which are economical and durable. |
| Powdered fertilizers (such as diammonium phosphate) | Wear-resistant rubber belt conveyor or PVC belt conveyor | Powdered fertilizers are highly abrasive, and wear-resistant rubber belts or PVC belts have better wear resistance and can extend the service life. |
| Corrosive fertilizers (such as ammonium sulfate) | Acid and alkali resistant rubber belt conveyor or fluoroplastic belt conveyor | Corrosive fertilizers will corrode the conveyor belts, and acid-resistant and alkali-resistant rubber belts or fluoroplastic belts have good corrosion resistance. |
| High-temperature fertilizers (such as some organic fertilizers) | High temperature resistant rubber belt conveyor or steel cord belt conveyor | High-temperature fertilizers will accelerate the aging of the belts, and high-temperature-resistant rubber belts or steel cord belts have better temperature resistance. |
| Viscous fertilizers (such as organic fertilizers) | Adhesion-resistant rubber belt conveyor or corrugated side plate belt conveyor | Sticky fertilizers are easy to adhere to the belts, and adhesion-resistant rubber belts or corrugated side plate belts can effectively prevent material adhesion. |
Fertilizer belt conveyors are essential equipment in the agricultural industry, transporting fertilizers efficiently from storage areas to fields. When selecting or designing a fertilizer belt conveyor, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
1. Fertilizer Type and Properties:
Particle Size: The size of fertilizer particles affects conveyor belt selection. Fine particles might require a different belt material or construction to prevent leakage.
Bulk Density: The density of the fertilizer determines the required belt width and horsepower for efficient transportation.
Abrasiveness: The abrasive nature of some fertilizers can accelerate belt wear. Choose a belt with a durable cover and appropriate backing.
Corrosiveness: If the fertilizer is corrosive, select a belt with a chemically resistant material.
2. Capacity Requirements:
Throughput: Determine the desired hourly or daily tonnage of fertilizer to be transported.
Peak Load: Consider the maximum expected flow rate, especially during busy seasons.
3. Distance and Elevation:
Length: The distance between the loading and unloading points affects the conveyor's length and horsepower requirements.
Inclination: If the conveyor needs to transport fertilizer uphill, the angle of inclination will influence the required power and belt design.
4. Environmental Factors:
Weather Conditions: Exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or precipitation can impact belt performance and durability.
Outdoor or Indoor Use: If the conveyor will be used outdoors, consider weatherproofing measures and materials.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.