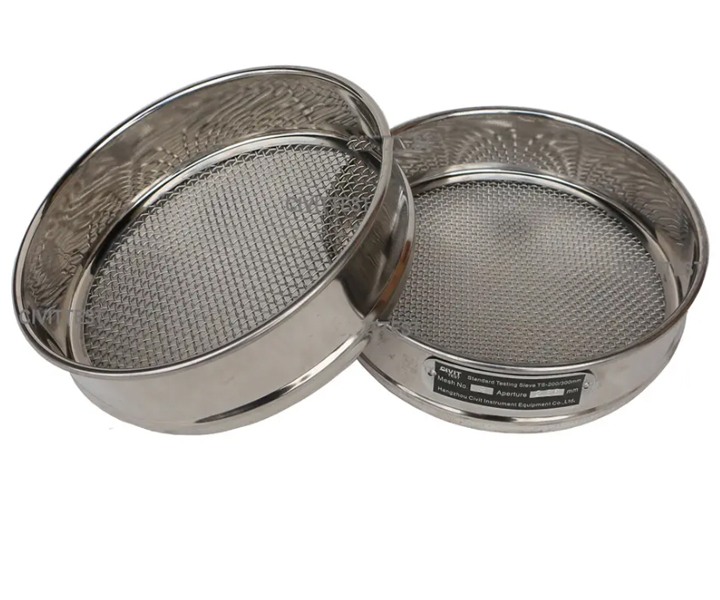
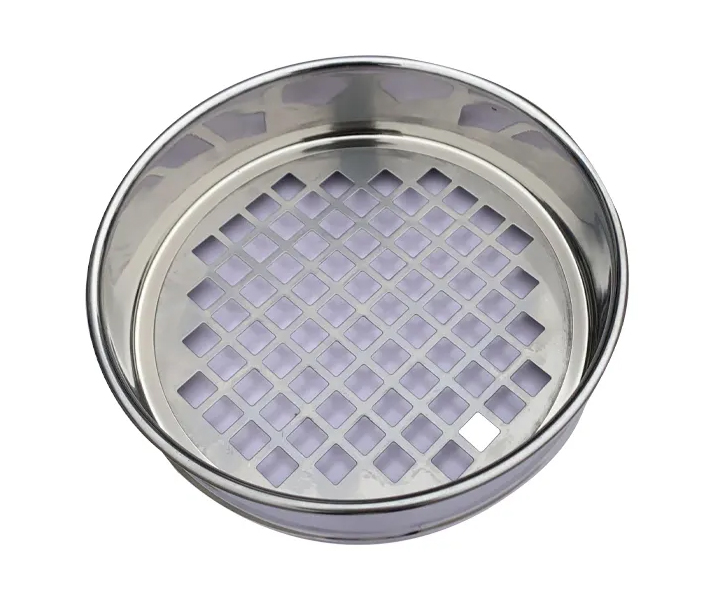
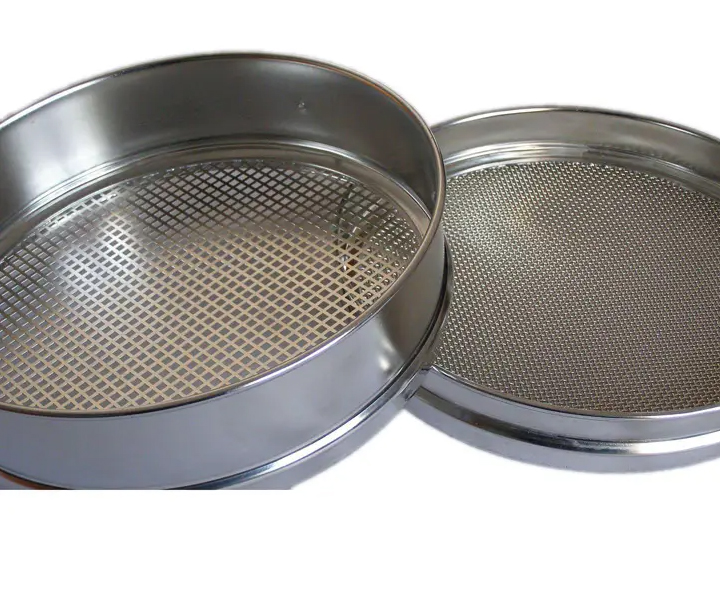
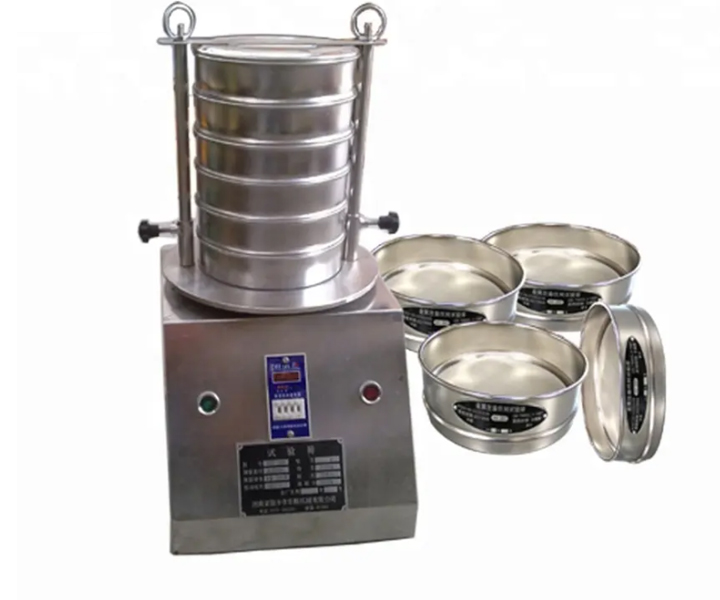










is an instrument for particle size measurement that can quickly and efficiently measure the size of solid particles from 125 mm to 20 μm
![]()
![]()
![]()
Price:$20.00-$3,680.00/Set/Set
Consult now and enjoy a 10% discount
Screen diameter: 75mm, 100mm, 200mm, 300mm, 400mm
Screen depth: 32, 50 or 65 mm
Measuring range: 20µm-125mm
Feeding amount: 200g
Screen frame layers: 1-8 layers
Amplitude: 1-4mm Voltage: 220V
Power: 0.125KW Noise: ≤50dB
Weight: 36 kg
Type: woven mesh (0.02mm-2.36mm) / perforated plate (: 1mm-125mm) / electroforming (75μm-5μm)
Material: stainless steel/brass/plastic
Sieve hole: round hole/square hole
Commitment:
Sieve analysis test is a common laboratory test used to determine the particle size distribution of a granular material. It involves passing a sample of the material through a series of sieves with progressively smaller openings, and measuring the weight of material retained on e ach sieve.
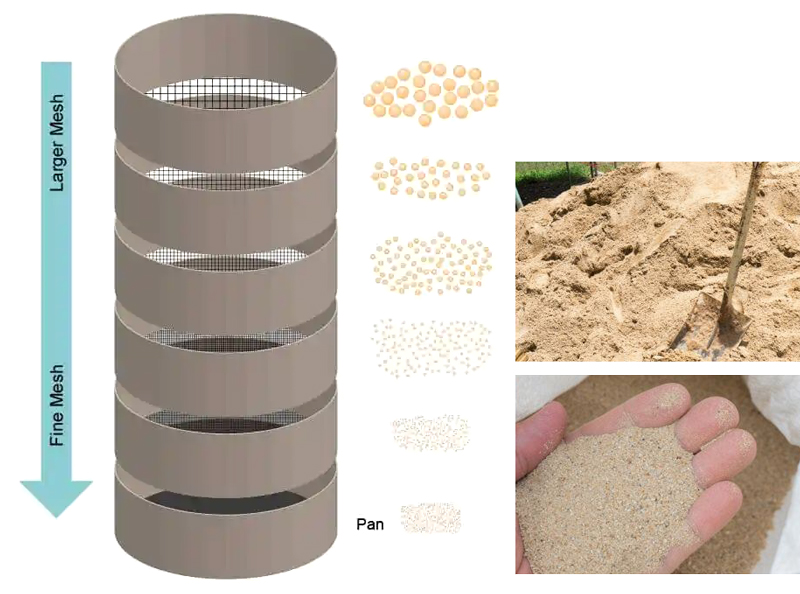

Sieve analysis test can separate and classify samples up to 2 kg in the measurement range of 20µm-63mm, with diameters of 75mm, 100mm, 200mm, 300mm, 400mm, divided into wire woven mesh test sieves (mesh size of 0.02mm-2.36 mm), metal perforated plate test sieves (screen size 1mm-125mm), electroformed test sieves (screen size 5μm-500μm), stainless steel, brass or nylon sieves can be selected according to actual use.
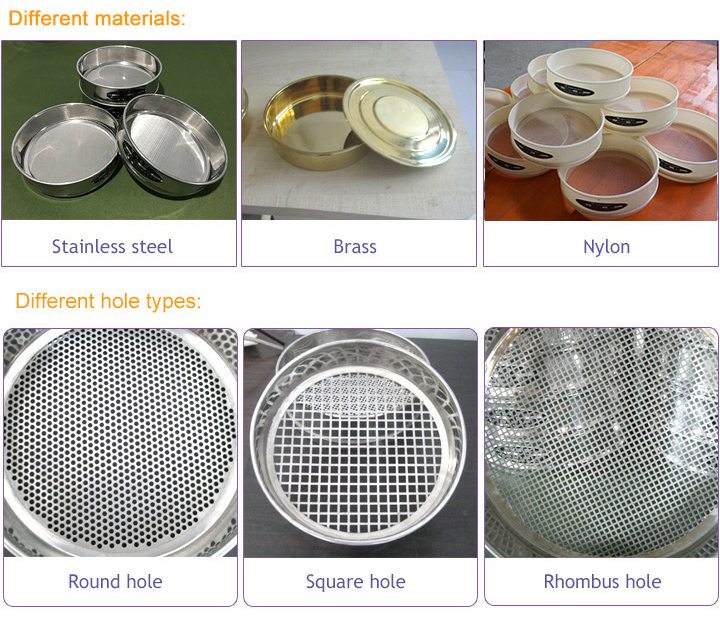
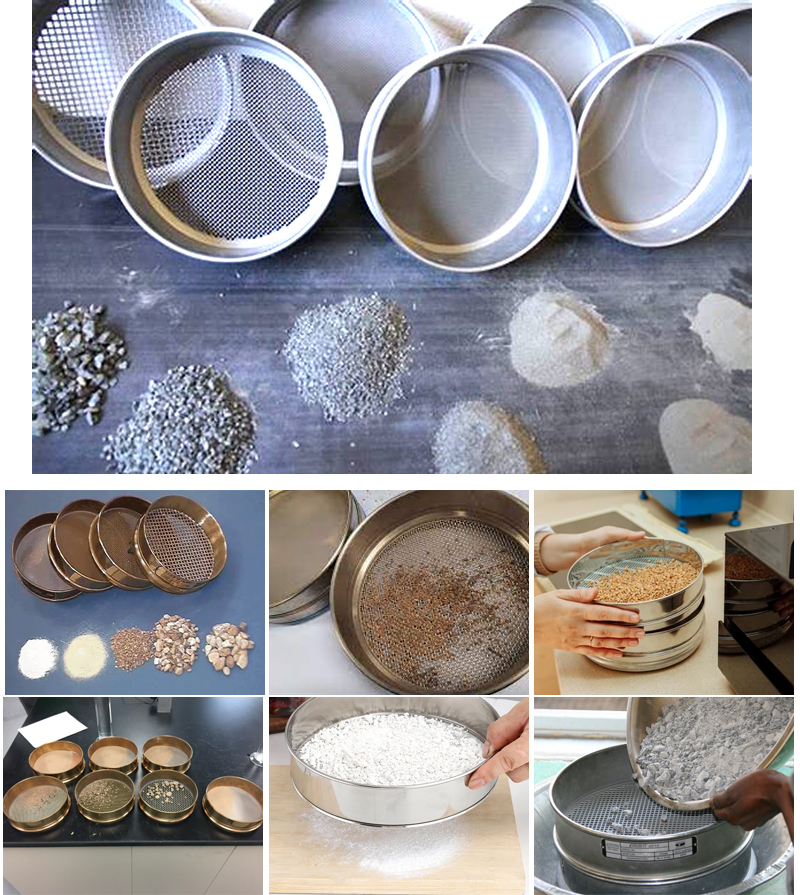


The purpose of a sieve analysis test is to determine the particle size distribution of a granular material. This test is commonly used in various industries such as construction, agriculture, mining and pharmaceuticals, where the particle size distribution of a material can significantly affect its properties and performance. Sieve analysis testing provides important information about the particle size distribution of a material and can help by:
1. Quality control: Through testing, the particle size distribution and quality of the material can be ensured to meet the required specifications. This is very important to ensure the consistency and performance of the material in various applications.
2. Material Characterization: This test can be used to characterize the properties of a material, including its density, porosity, and permeability. This information can be used to optimize materials for specific applications.
3. Process control: This test can be used to monitor and control the particle size distribution of materials during processing. This is important to ensure that the material is machined to the desired size range and to prevent over- or under-grinding.
4. Research and development: Through testing, the particle size distribution of different materials can be studied, and new materials with specific properties and performances can be developed.
The steps involved in conducting a sieve analysis test are:
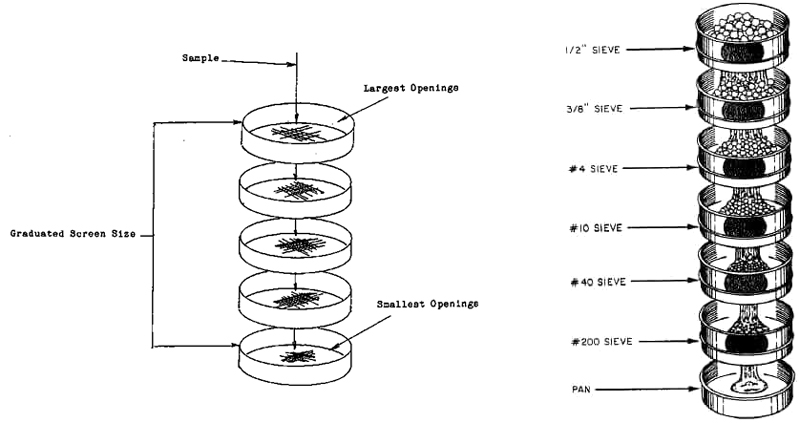
1. Collect a representative sample of the material to be tested, ensuring that it is dry and free of any contaminants or debris.
2. Weigh the sample and record the weight.
3. Set up a stack of sieves with the smallest opening size at the bottom and the largest at the top. The number of sieves used will depend on the size range of the particles being tested.
4. Place the sample on the top sieve and cover it with a lid.
5. Shake the stack of sieves using a sieve shaker or by hand for a specified amount of time, typically around 10-15 minutes.
6. Weigh the material retained on each sieve and record the weight.
7. Calculate the percentage of material retained on each sieve by dividing the weight retained by the total weight of the sample and multiplying by 100.
8. Plot the particle size distribution on a graph by plotting the percentage of material retained on each sieve against the sieve opening size.
Sieve Analysis Test of Soil
Sieve Analysis Test for Coarse Aggregate
Quality control
Helps ensure that materials meet specifications for particle size distribution and quality requirements. This is very important to ensure the consistency and performance of the material in various applications.
Material Characterization
The test provides information on the properties of the material, including its density, porosity and permeability. This information can be used to optimize materials for specific applications.
Precise mesh
All standard sieves are interchangeable and consistent. The same number of sieves in different periods ensures consistent mesh. The same number of sieves in different periods ensures consistent mesh.
High temperature resistant
The screen mesh and the screen frame are connected by welding, which can withstand high temperature of 400° and can be used for inorganic and organic solutions. The connection is firm, without gaps, and without materials.
Cut costs
This helps to optimize raw material usage by ensuring that raw material is processed to the required size range and waste is minimized.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory agencies often require sieve analysis testing to ensure materials meet specifications for quality and safety requirements.

When purchasing a test sieve, the following are some common available options that can be selected according to specific experimental needs:
Screen material: Stainless steel, copper, nylon, etc., you can choose the appropriate screen material according to the characteristics of the material.
Vibration mode: There are electric vibration, ultrasonic vibration, and slapping, etc., choose the appropriate vibration mode according to the characteristics of the sample and experimental needs.
Digital control: Some test sieves are equipped with a digital control panel, which can accurately control vibration parameters, sieving time, etc., to improve experimental accuracy.
Multi-layer screen: Some test sieves have a multi-layer screen design, which can screen multiple particle sizes at the same time.
| No. | Technical | Technical indicate |
| 1 | Sieve Diameter | 200mm 8inch/300mm 12inch |
| 450mm 18inch/100mm4inch/75mm 3inch | ||
| 2 | Material | Stainless steel or Brass |
| 3 | Inner height | 50mm and 60mm |
| 4 | Aperture size range | 0.02mm to 125mm |
| 5 | Hole model | Wire mesh and perforated plate |
| 6 | Detail aperture | 125, 106, 100, 90, 75, 63, 53, 50, 45, 37.5, 31.5, 25, 22.4, 19, 16, 13.2, 12.5, 11.2, 9.5, 8, 6.7, 6.3, 5.6, 4.75, 4, 3.35, 2.8, 2.36, 2, 1.7, 1.4, 1.18, 1, 0.85, 0.71, 0.6, 0.5, 0.425, 0.355, 0.3, 0.25, 0.212, 0.18, 0.15, 0.125, 0.106, 0.09, 0.075, 0.063, 0.053, 0.045, 0.038mm etc. |
| 7 | Use | Grading Standard Testing Sieve Test Sieve for soil test sieve, aggregate sieve, concrete test sieve, cement test sieve, asphalt test sieve, wet sieve, wire mesh sieve, perforated sieve, astm sieve, en sieve |
| No. | Type | Mesh(mm) | No. | Type | Mesh(mm) |
| 1 | 8# | 2.360 | 15 | 70# | 0.212 |
| 2 | 10# | 2.000 | 16 | 80# | 0.180 |
| 3 | 12# | 1.700 | 17 | 100# | 0.150 |
| 4 | 14# | 1.400 | 18 | 120# | 0.125 |
| 5 | 16# | 1.180 | 19 | 140# | 0.106 |
| 6 | 18# | 1.000 | 20 | 170# | 0.09 |
| 7 | 20# | 0.850 | 21 | 200# | 0.075 |
| 8 | 25# | 0.710 | 22 | 230# | 0.063 |
| 9 | 30# | 0.600 | 23 | 270# | 0.053 |
| 10 | 35# | 0.500 | 24 | 325# | 0.045 |
| 11 | 40# | 0.425 | 25 | 400# | 0.038 |
| 12 | 45# | 0.355 | 26 | 500# | 0.028 |
| 13 | 50# | 0.300 | 27 | >500# | <0.028 |
Common screen materials include but are not limited to the following:

Stainless steel screen: It is corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant, suitable for screening most granular materials.
Brass: Brass screen is often used in some screening occasions where the requirements for granular materials are not strict.
Copper: Copper screen has certain corrosion resistance and conductivity, suitable for screening some special granular materials.
Nickel: Nickel screen is usually used in some occasions with high requirements for high temperature resistance.
Polyethylene: Polyethylene screen has good corrosion resistance and wear resistance, suitable for screening needs in some special occasions.
Metal alloy: It has high hardness and wear resistance, suitable for occasions with high requirements for granular materials.
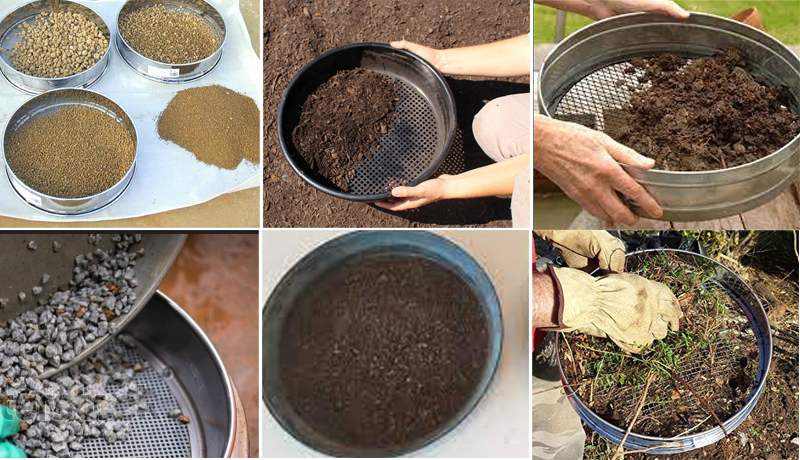

| Cassia | 14 mesh | Buckwheat | 12 mesh | Tenebrio molitor eggs | 12 mesh |
| Worm dung | 30 mesh | Soybeans | 4-5 mesh | green beans | 10 mesh |
| Rice | 12-14 mesh | rice flour | 30-40 mesh | Cornmeal | 30-40 mesh |
| flour | 50-60 mesh | Miscellaneous grains | 40-50 mesh | Sesame Millet | 22-24 mesh |
| Fried Chicken Burger Breaded | 20-30 mesh | Mung bean flour | 40-50 mesh | Sesame powder | 40-50 mesh |
| Notoginseng powder | 100-120 mesh | Pine pollen | 100-120 mesh | Chinese medicine powder | 40-50 mesh |
| Oral Chinese medicine powder | 60-80 mesh | Traditional Chinese Medicine Mask | 80-120 mesh | Pearl powder | 120-150 mesh |
| Medicine residue | 60-150 mesh | Soy milk | 80-120 mesh | honey | 80-120 mesh |
| Soup dregs | 120-150 mesh | Tea water | 120-150 mesh | Cooking oil | 150-200 mesh |
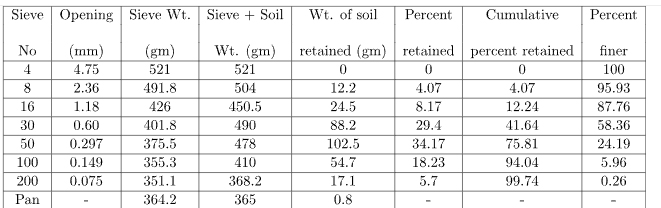
The results of a sieve analysis test provide information about the particle size distribution of a granular material. The test results typically include the following information:
1. Mass retained on each sieve: The mass retained on each sieve is reported in grams or ounces and represents the weight of material that was retained on that particular sieve.
2. Cumulative mass retained: The cumulative mass retained is the total weight of material retained on all the sieves up to that point in the sieve stack.
3. Cumulative mass percent retained: The cumulative mass percent retained is the percentage of material retained on all the sieves up to that point in the sieve stack, calculated by dividing the cumulative mass retained by the initial sample mass and multiplying by 100.
4. Cumulative mass percent passing: The cumulative mass percent passing is the percentage of material that has passed through all the sieves up to that point in the sieve stack, calculated by subtracting the cumulative mass percent retained from 100%.
5. Particle size distribution curve: The particle size distribution curve is a graph that shows the percentage of material retained on each sieve plotted against the sieve size (either in millimeters or microns). This curve provides a visual representation of the particle size distribution of the material.
The results of the sieve analysis test can be used to determine the particle size distribution of the material and to classify it according to various standards and specifications. This information can be useful for quality control, process control, material characterization, and research and development in various industries.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.