Wet sieving analysis is a commonly used particle size analysis method. It places the sample in a liquid medium (usually water) and uses the difference in sieve aperture to separate particles of different sizes, thereby obtaining the particle size distribution.
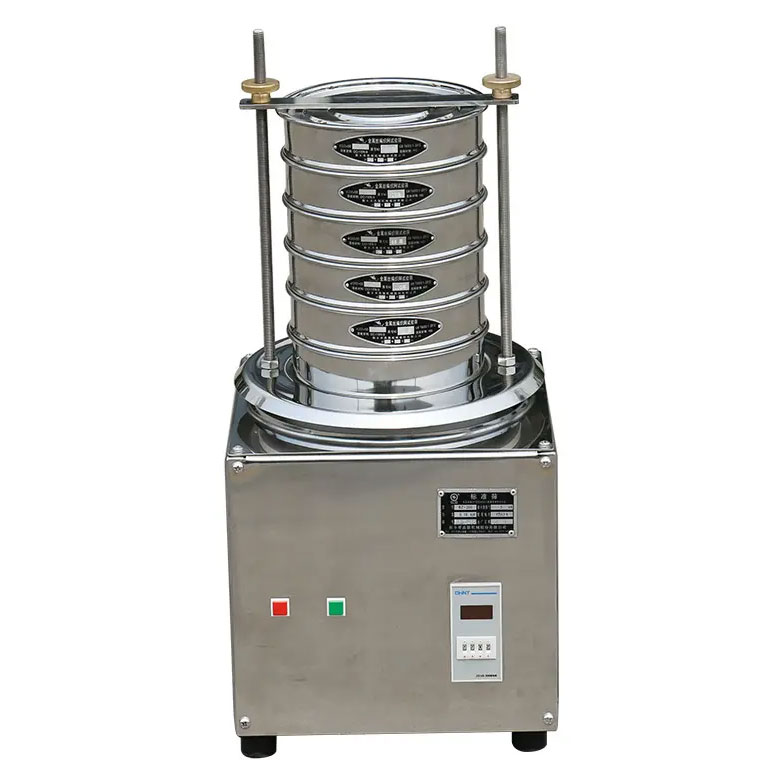

Wet sieving is a method of separating coarse material from water or another liquid, followed by drying, identification and analysis. It is a method that can be used to prepare samples, for example, to remove fines, break down agglomerates or eliminate static charges. During this process, the sample is washed through the sieve pack. Sieving and washing can be performed together using a sieving machine.
Wet sieving is a pretreatment method suitable for solid samples that are water-insoluble, water-stable, and thermally stable (below 110°C). By sieving in water, fine particles in the sample that are easy to agglomerate and difficult to dry sieve can be effectively removed, thereby improving the accuracy of subsequent sieving analysis. Before normal drying and testing of samples, wet sieving can be used to remove fine materials that may be difficult to sieve.
The principle of wet sieving analysis is similar to that of dry sieving analysis, both of which use the sieving effect of the sieve holes to separate particles of different particle sizes. However, wet sieving analysis is carried out in a liquid medium, and the liquid can play the following roles:
1.Disperse particles: Liquid can effectively disperse particles in the sample, reduce the interaction between particles, prevent particle agglomeration, and improve sieving efficiency.
2.Reduce static electricity: Liquid can effectively reduce the static electricity between particles and prevent particles from adhering to the sieve.
3.Improve sieving conditions: Liquid can lubricate the sieve, reduce clogging of the sieve holes, and improve sieving accuracy.
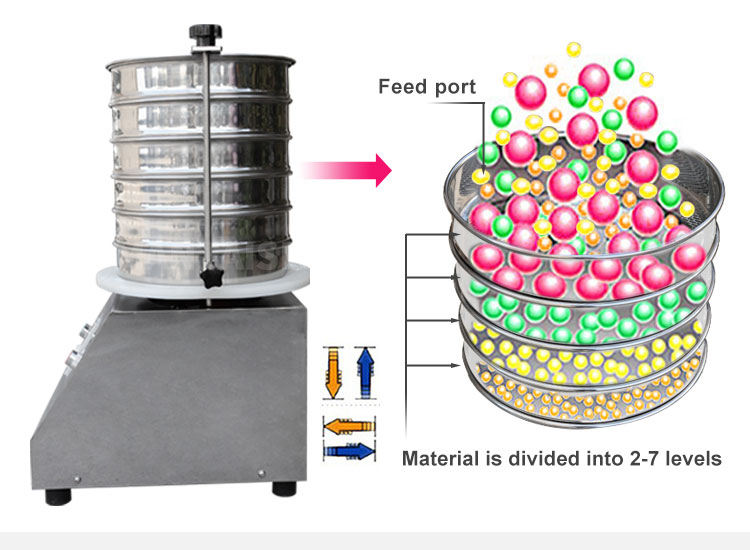
1.When dry sieving does not produce a sufficient degree of sample separation
2.When testing samples containing small amounts of gravel-sized material
3.When silt and clay need to be removed
| Feature | Wet sieve analysis | Dry sieve analysis |
| Medium | Water | other liquid Air |
| Applicablescope | Samples that are easy to agglomerate, have a high content of fine powder, and are viscous, samples that are insoluble in water and water-resistant. | most dry solid samples |
| Advantages | It can effectively disperse the sample, reduce the clogging of the sieve holes, and improve the screening efficiency; it is suitable for fine-grained samples. | It is simple to operate and has low equipment cost. |
| Disadvantages | Requires additional washing and drying steps,not suitable for samples that are easily soluble in or affected by water. | It is easy to generate static electricity, which causes particles to agglomerate and affects the screening results; it is not suitable for samples that are prone to agglomeration. |
| Operation process | Place the sample in the sieve and vibrate in water to sieve. | Place the sample directly in the sieve and sieve by vibration or sieving machine. |
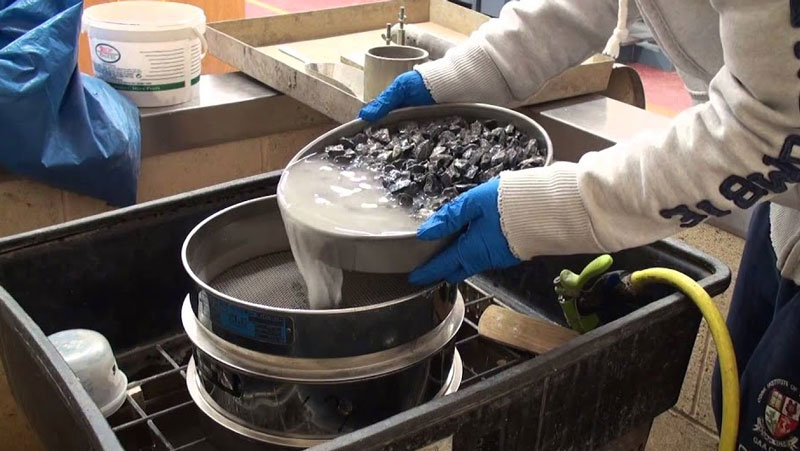

1.Pre-testing
Mix the sample material with water until it becomes a suspension
Prepare a stack of soaked sieves
place gaskets between each individual sieve
Place the wet cleaning cover on top of the sieve and the wet cleaning receiver (with outlet) on the bottom
build water flow
2.wet sieving
Pour the ingredients over the upper sieve
Open the sieving machine for 5-10 minutes according to the sample size
turn on the water supply
Observe the liquid at the outlet, once the liquid clears, turn off the water and the vibrator
Collect material retained on each sieve
Use an oven to dry the material. After drying, the material needs to be weighed for data analysis.

Wet sieving can be done manually by propping a stack of test sieves over a sink, or by passing water through a stack of sieves on a shaker.
However, care needs to be taken to prevent water spillage as this may result in sample loss. Fine mesh test sieves (below 100 μm) are more prone to spillage. Users are advised to use specially designed accessories for wet sieving. For example:
Wet cleaning test sieve
Wet cleaning test sieves are manufactured with extra deep frames for wet sieving.
Test sieve with rubber gasket
Gaskets are recommended between individual test sieves to prevent leakage and loss of liquid or sample material.
Wet cleaning covers and receivers
The wet cleaning cap and receiver are designed with adapters to allow the liquid to flow with the waste.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.