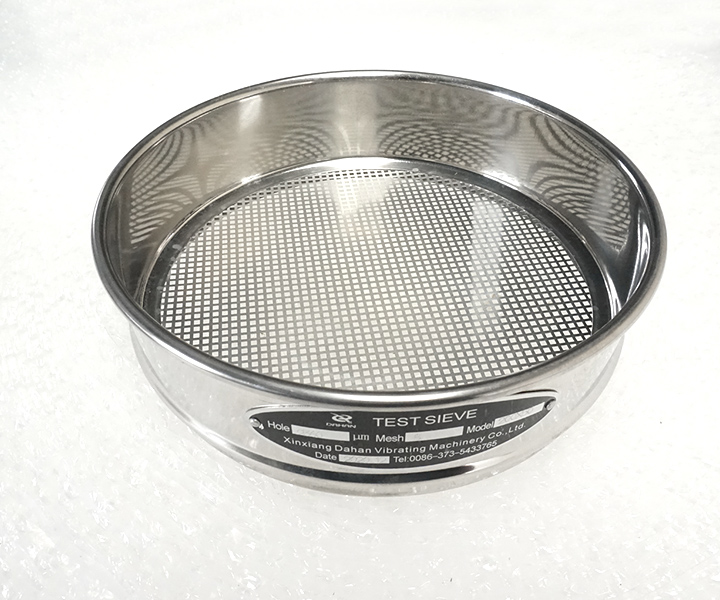
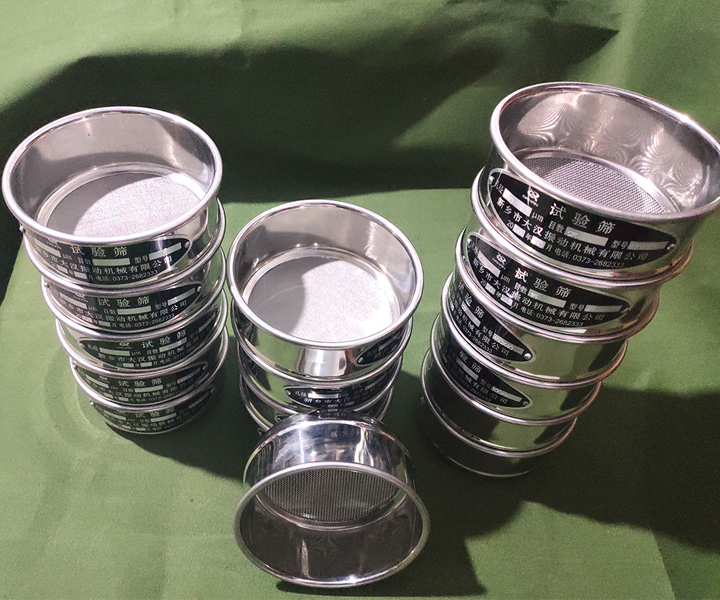
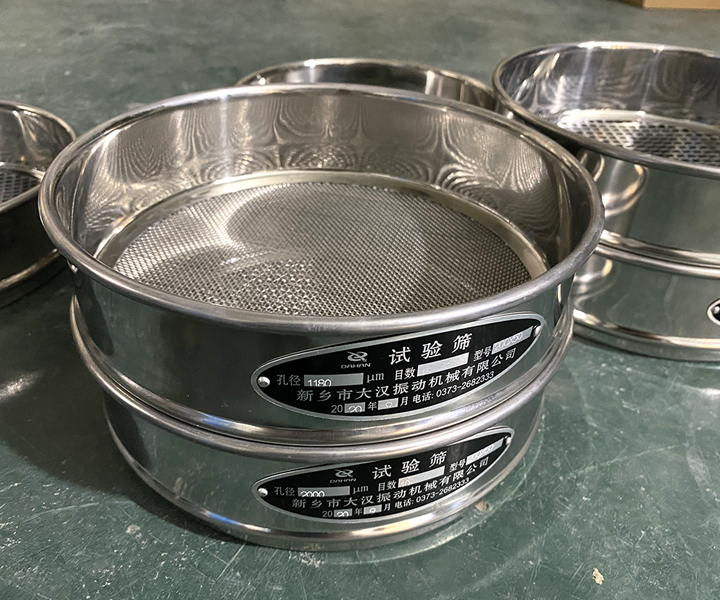
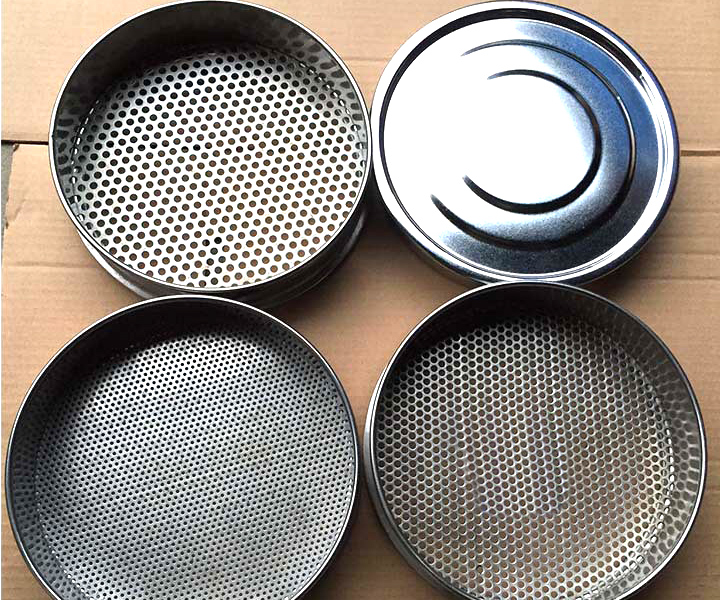
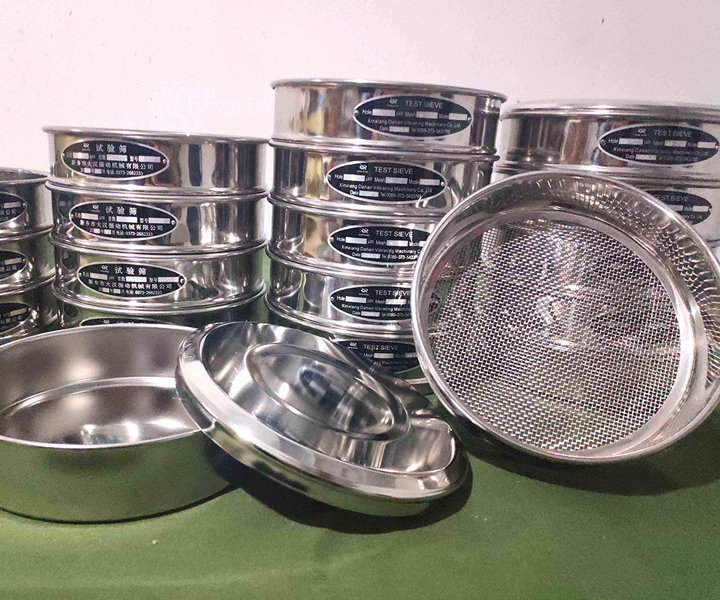










Particle size analysis and classification of powder and granular materials in the laboratory
![]()
![]()
Price:$22.00-$68.00/Set
Consult now and enjoy a 10% discount
Diameter: 6, 8, 10, 12, 24 inches, 15cm 20cm 30cm 35cm 40mm or customized
Height:5mm, 8cm or customized
Size: 1 micron-2000 micron
Screening particle size: 0.038-3mm
Feeding amount: ≤200g
Material: SUS304, SS316 stainless steel, brass or customized
International standard: ISO3310-1: 1990 R20/3, R20, R40/3 series
Application: Laboratory testing and analysis of sand, soil, aggregate, etc.
Commitment:
Sieve analysis is a technique used to determine the particle size distribution of a sample of material. In this technique, a sample of material is passed through a series of sieves of decreasing mesh size and the amount of material retained on each sieve is measured. The sieves are stacked in descending order of mesh number, with the finest mesh at the bottom and the coarsest mesh at the top.

Sieve analysis is a commonly used technique in many industries, including construction, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, for the characterization and quality control of materials. It provides valuable information about the particle size distribution of a sample, which is important for many applications such as designing construction materials, optimizing processing conditions, and ensuring product quality and consistency.
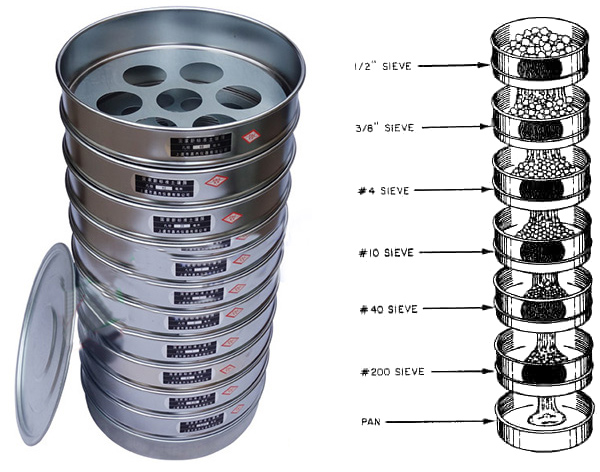
Large sample volume: Sieving analysis is suitable for analyzing large batches of samples.
A rough understanding of particle size distribution: Sieving analysis can quickly obtain particle size distribution information of samples.
Need to separate samples of different particle sizes: Sieving analysis can separate particles of different particle sizes.
Limited cost budget: Sieving analysis equipment investment is small.
1. Particle size distribution analysis: This is the most basic purpose of screening analysis. Through screening, the percentage of particles of different particle sizes in the sample can be obtained, and the particle size distribution curve can be drawn to intuitively reflect the particle size composition of the material.
2. Material property evaluation: Particle size distribution directly affects the physical properties of the material, such as fluidity, bulk density, etc. Through screening analysis, these properties of the material can be evaluated to provide a basis for the selection and use of the material.
3. Quality control: During the production process, the particle size of the product can be controlled through screening analysis to ensure the stability of product quality.
4. Process optimization: During the process of crushing, grinding, etc., screening analysis understands the particle size changes of the material, thereby optimizing the process parameters.
5. Environmental monitoring: Screening analysis can be used to separate particles of different particle sizes in order to analyze pollutants of different particle sizes.
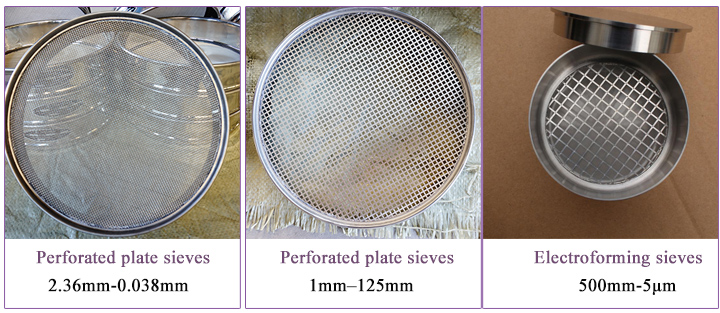
There are two main types of sieve analysis:
1. Dry Sieve Analysis: In dry sieve analysis, the sample is dried and then passed through a series of sieves with decreasing mesh size. The sieves are stacked in order of decreasing mesh size, with the finest mesh at the bottom and the coarsest mesh at the top. The sample is placed on the top sieve, and the stack of sieves is then shaken manually or mechanically for a certain period of time. The amount of material that is retained on each sieve is measured and recorded.
2. Wet Sieve Analysis: In wet sieve analysis, the sample is suspended in a liquid, typically water, and then passed through a series of sieves with decreasing mesh size. The sieves are stacked in order of decreasing mesh size, with the finest mesh at the bottom and the coarsest mesh at the top. The sample is placed on the top sieve, and the stack of sieves is then shaken manually or mechanically for a certain period of time. The liquid and the material that passes through the sieves are collected separately, and the amount of material that is retained on each sieve is measured and recorded.

Particle size by sieve analysis can be determined by following these steps:
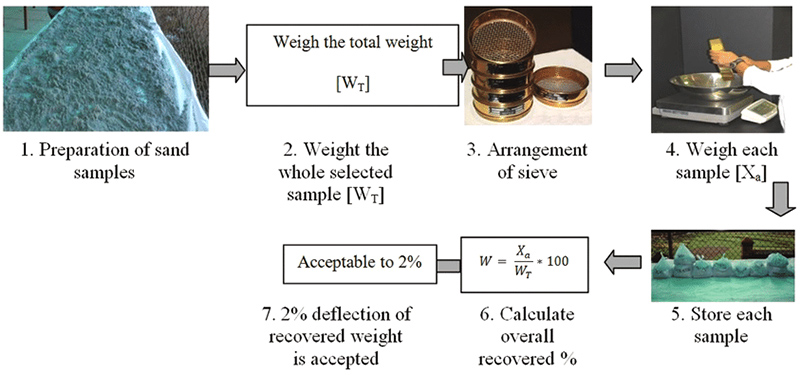
1. Prepare the Sample: Obtain a representative sample of the material to be analyzed and ensure that it is properly homogenized. If necessary, dry the sample to remove any moisture.
2. Select the Sieves: Choose a set of sieves with a range of mesh sizes that covers the expected particle size range of the sample. The sieves should be stacked in order of decreasing mesh size, with the finest mesh at the bottom and the coarsest mesh at the top.
3. Weigh the Sieves: Weigh each sieve and record the weight.
4. Perform the Sieve Analysis: Place the sample on the top sieve, and then shake the stack of sieves manually or with a mechanical shaker for a specified length of time. The shaking action causes the smaller particles to pass through the smaller mesh openings of the sieves, while the larger particles are retained on the sieves with larger mesh openings. After shaking, remove each sieve from the stack and weigh the amount of material retained on it. Record the weight of each sieve and the amount of material retained on it.
5. Calculate the Particle Size Distribution: Calculate the percentage of material that is retained on each sieve by dividing the weight of the material retained on each sieve by the total weight of the sample and multiplying by 100. Plot the particle size distribution curve by graphing the percentage of material retained on each sieve versus the sieve size.
6. Analyze the Results: Analyze the particle size distribution curve to determine the mean particle size, the particle size range, and the uniformity of the sample.
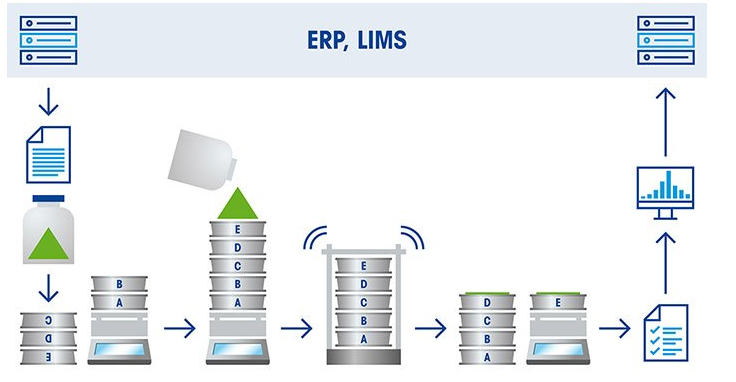
Sieve analysis is a widely used technique in many industries for the characterization and quality control of materials. The following are some common applications of sieve analysis:

1. Construction materials: used to determine the particle size distribution of construction materials such as sand, gravel and crushed stone. Particle size distribution is important for designing and optimizing the properties of these materials, such as their strength, processability and permeability.
2. Food processing: Used in the food processing industry to determine the particle size distribution of ingredients such as flour, sugar and spices. Particle size distribution affects the properties of these ingredients, such as their flowability, texture and taste.
3. Pharmaceuticals: Used in the pharmaceutical industry to determine the particle size distribution of active ingredients and excipients. Particle size distribution affects the bioavailability and efficacy of pharmaceutical formulations.
4. Environmental monitoring: for environmental monitoring to determine the particle size distribution of air and water particles. Particle size distribution affects the transport and deposition of particulate matter, with environmental and health implications.
5. Chemistry and Minerals: Used in the chemical and mineral industries to determine the particle size distribution of powders, crystals and granules. Particle size distribution affects the properties of these materials such as their reactivity, solubility and flow.
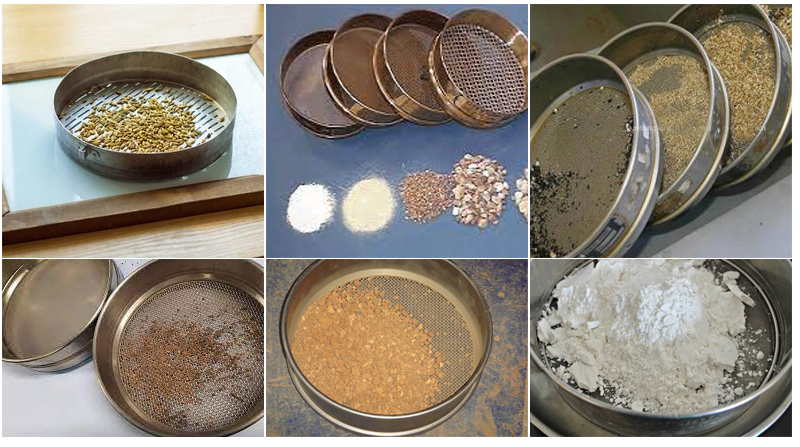
sieve analysis of sand
sieve analysis of soil
sieve analysis of aggregates
The need to detect the mesh size of the screen frame is less than the mesh aperture of the material particles are screened to the lower screen frame, so that each layer of test screen only the same size of the material, to achieve the separation of different size and determine the size of the material composition.
Steps of sieve analysis:
1. According to the material to be inspected and the corresponding standards to determine the standard sieve to be selected.
2. The sieve according to the aperture from large to small, from the bottom to the top in turn stacked on the tray seat, by the groove or positioning screw on the standard screen positioning.
3. Put the material to be checked into the top sieve, and then press the standard sieve.
4. Put the timer switch in the corresponding position, (pay attention to read the timer instructions, different Settings set the time is different) and then turn on the power switch, sieve analysis will start to work.
5. After the work of the screen stops, unscrew the nut on the wire pillar, remove the sieve head, and carefully remove the sieve.
6. Turn off the power.

Vibratory sieving: the sample is thrown upward by the vibration at the bottom of the screen and then falls back under the action of gravity.
Horizontal sieving: The screen moves in a horizontal circle in a plane with almost no particles changing its direction on the screen. It is suitable for needle, flat, long or fibrous samples.
Tap sieving: It also uses horizontal circular motion, but adds to the regular vertical sieving, just like with the hand.

| No. | Type | Mesh(mm) | No. | Type | Mesh(mm) |
| 01 | 8# | 2.36 | 15 | 70# | 0.212 |
| 02 | 10# | 2 | 16 | 80# | 0.18 |
| 03 | 12# | 1.7 | 17 | 100# | 0.15 |
| 04 | 14# | 1.4 | 18 | 120# | 0.125 |
| 05 | 16# | 1.18 | 19 | 140# | 0.106 |
| 06 | 18# | 1 | 20 | 170# | 0.09 |
| 07 | 20# | 0.85 | 21 | 200# | 0.075 |
| 08 | 25# | 0.71 | 22 | 230# | 0.063 |
| 09 | 30# | 0.6 | 23 | 270# | 0.053 |
| 10 | 35# | 0.5 | 24 | 325# | 0.045 |
| 11 | 40# | 0.425 | 25 | 400# | 0.038 |
| 12 | 45# | 0.355 | 26 | 500# | 0.028 |
| 11 | 50# | 0.3 | 27 | >500# | 0.028 |
| 14 | 60# | 0.25 |
1. Wide range of applications: Sieving analysis is applicable to all types of granular materials, whether powder or bulk, they can be analyzed by sieving.
2. Good repeatability: The sieving results have good repeatability, and multiple repeated experiments can be performed to verify the reliability of the results.
3. Separation of samples: Sieving can not only obtain particle size distribution data, but also separate particles of different sizes for subsequent analysis.
4. Intuitive results: The screening results are expressed as the mass of particles of different particle sizes, without the need for complex calculations.


Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.