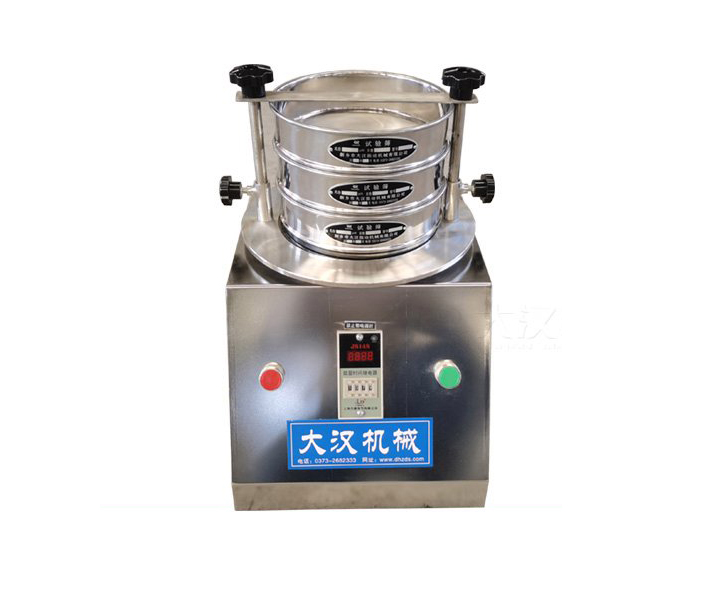
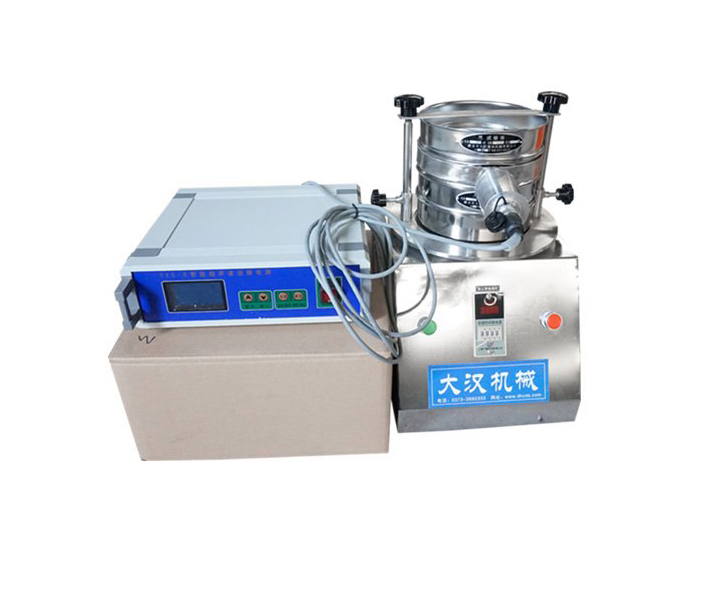
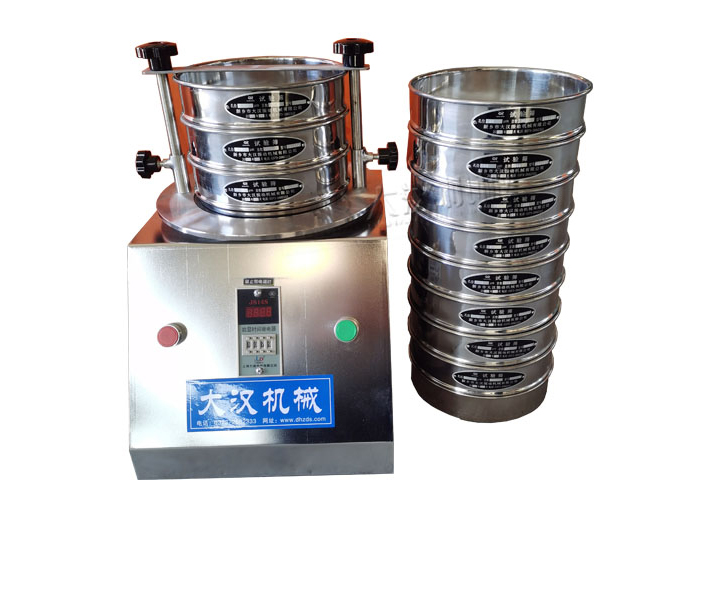
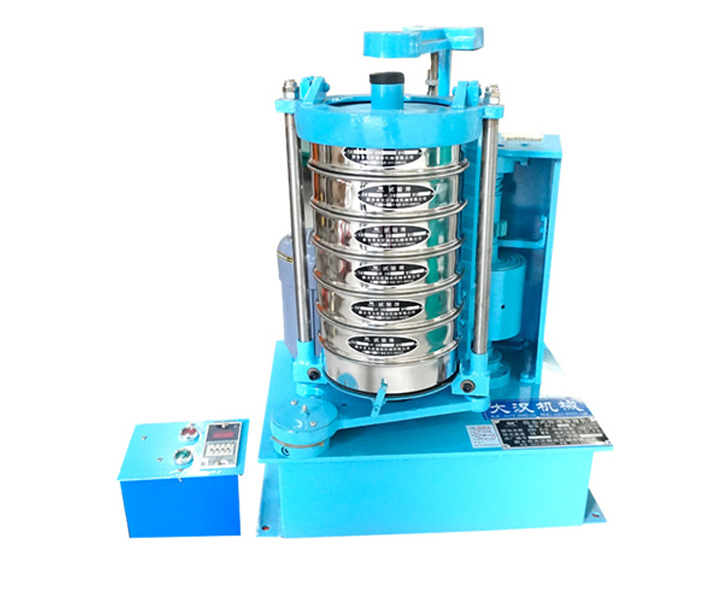
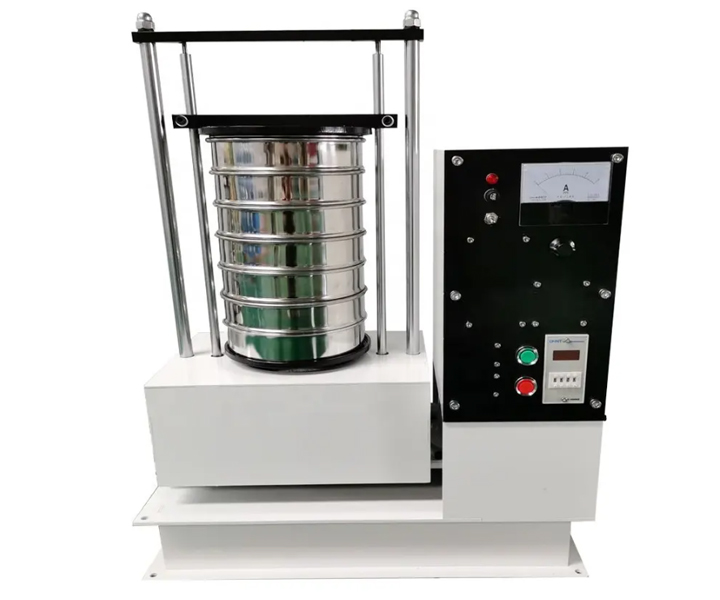










For classification and particle size determination of powders, bulk granules and suspensions in the laboratory
![]()
![]()
![]()
Price:$20.00-$3,680.00/Set/Set
Consult now and enjoy a 10% discount
Sieve diameter: 75mm, 100mm, 200mm, 300mm, 400mm, 500mm
Measuring range: 20µm-125mm
Feeding amount: 200g
Screen frame layers: 1-8 layers
Amplitude: 1-4mm Voltage: 220V
Power: 0.125KW Noise: ≤50dB
Dimensions: 360*300*736 Weight: 36 kg
Application: Used in scientific research and production, laboratories, quality inspection rooms and laboratories of colleges and universities to screen, filter and detect the particle size structure, liquid solid content and sundry content of granular and powdery materials
Commitment:
Particle size test is a process that involves measuring and analyzing the size distribution of particles within a sample. It is an important analysis in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, mining, food processing, cosmetics, and environmental monitoring.
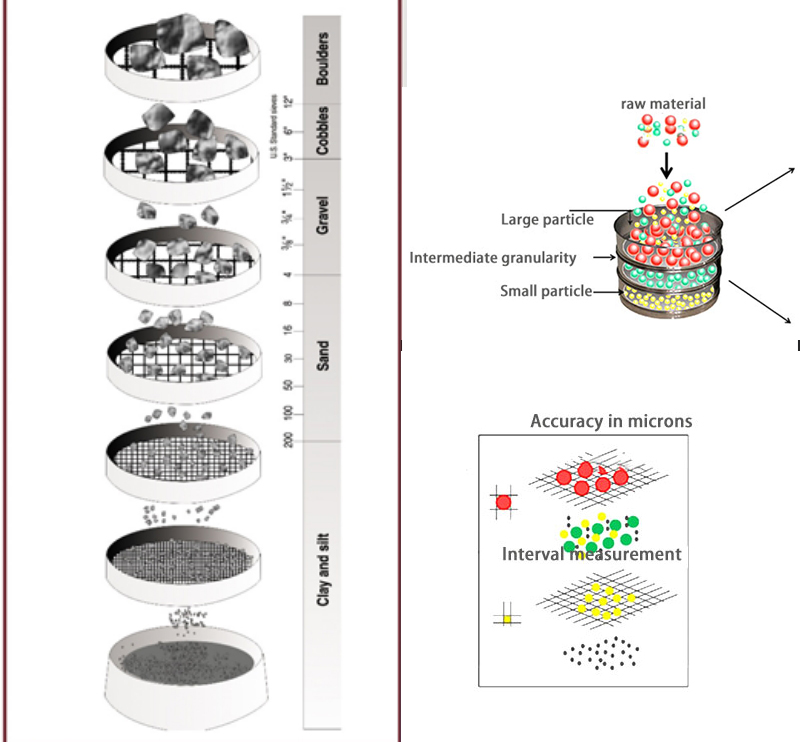
Particle size test is produced in strict accordance with GB6003.1-1997 or GB6003.2-1997 standards and is used for particle size classification and detection of powders, granules or suspensions. It can quickly and effectively measure the size of solid particles from 150mm to 5μm. Particle size test diameters include 75mm, 100mm, 200mm, 300mm, and 400mm. Standard sieves between 200mm and 300mm are more common. In addition, stainless steel, nylon, and all-copper sieve frames can be selected according to requirements.


Particle size test is a commonly used screening tool for particle size analysis and screening of granular materials. Here are several common screening methods:
1. Dry sieving test: Place the dry particle sample on the test sieve, and use mechanical vibration or shock to separate and classify the particles in the sieve holes. Suitable for screening coarse particles and dry samples.
2. Wet sieving test: Place the particle sample containing moisture on the test sieve, and sieve through water flushing or spraying. Suitable for screening sticky, moist or cohesive samples.
3. Vibration screening test: Granular samples are separated and classified in the sieve holes through mechanical vibration. Vertical vibrating screening or horizontal vibrating screening can be used.
Particle size testing is important for several reasons:

1.Product Performance and Quality: The particle size of a material can significantly impact its performance and quality. For example, in pharmaceuticals, the particle size of a drug can affect its dissolution rate and bioavailability. In food processing, the particle size of ingredients can affect product texture, taste, and stability. By understanding and controlling particle size, manufacturers can ensure consistent product quality and performance.
2.Process Optimization: Particle size analysis plays a crucial role in optimizing manufacturing processes. By studying the particle size distribution, engineers and operators can make adjustments to parameters such as grinding time, screen mesh sizes, and classification techniques to achieve the desired particle size distribution. This optimization can lead to improved process efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and better product consistency.
3.Quality Control: Particle size testing is an important aspect of quality control in various industries. By monitoring and controlling particle size, manufacturers can ensure that materials meet specific size specifications and comply with industry standards and regulations. This helps in maintaining consistent product quality and preventing issues such as segregation, clogging, or poor flowability.

Particle size test has various applications in different industries, some of which are:
1. Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, particle size test is used to ensure consistent drug delivery and bioavailability. The particle size distribution can affect the dissolution rate and absorption of the drug in the body, and thus it is important to control the particle size during drug formulation and manufacturing.
2. Food: In the food industry, particle size test is used to control the texture, mouthfeel, and appearance of the product. For example, in the production of chocolate, the particle size of the cocoa powder affects the smoothness and creaminess of the chocolate.
3. Cosmetics: In the cosmetic industry, particle size test is used to control the stability, texture, and appearance of the product. For example, in the production of creams and lotions, the particle size of the emulsions affects the creaminess and spreadability of the product.
4. Mining: In the mining industry, particle size test is used to optimize mineral processing and extraction. The particle size distribution can affect the efficiency of grinding, flotation, and leaching, and thus it is important to control the particle size during the mining and processing of ores.
5. Environmental monitoring: In environmental monitoring, particle size test is used to monitor the concentration and distribution of pollutants in air, water, and soil. The particle size distribution can affect the transport and fate of pollutants in the environment, and thus it is important to measure the particle size to understand the potential risks to human health and the environment.
Particle size analysis can be done using various methods, depending on the size range of the particles, the type of material, and the required accuracy and sensitivity of the results. The material is passed through a set of sieves of different apertures, and the The retained material is weighed. The results are used to calculate the particle size distribution based on the weight percent retained on each sieve. Sieve analysis is a simple and cost-effective method for analyzing particles in the millimeter to centimeter range.
Granular materials can be divided into different particle size levels according to the size of the sieve holes. The screening particle size classification of granular materials usually includes coarse particles, medium particles, fine particles and powder. Coarse particles generally refer to particles with a diameter greater than 4.75 mm, medium particles have a diameter between 4.75 mm and 0.075 mm, fine particles have a diameter between 0.075 mm and 0.002 mm, and powder refers to particles with a diameter less than 0.002 mm. Particles of different size classes have different uses and properties in engineering and scientific fields, so particle size classification is crucial for the handling and application of granular materials.
Particle size test of soil
Particle Size Test of Coarse Aggregate

Simple and cost-effective
Sieve analysis is a relatively simple and cost-effective method of particle size analysis. It requires minimal equipment and can be performed using standard laboratory sieves.
Wide range of sizes
It can analyze particles in the millimeter to centimeter range and can quickly and efficiently measure solid particle sizes from 125mm to 20μm, making it suitable for a wide range of materials and applications.
Accurate and reliable
is an accurate and reliable method for particle size analysis provided the sieves are calibrated and the sample is properly prepared and dispersed.
Standardized method
Sieve analysis is a widely accepted and standardized method of particle size analysis and is recognized by several international organizations such as ASTM International and ISO.
| NO. | Name | Unit | Parameter |
| 1 | frame diameter | mm | φ200 |
| 2 | the number of layer | s | 1~8 |
| 3 | sieve size | mm | 0.025-3 |
| 4 | vibrating amplitube | mm | 1~4 |
| 5 | vibration frequency | n/min | 1440 |
| 6 | power supply | V;HZ;KW | 220;50;0.12 |
| 7 | outside dimension | LWH | 350*350*(300+n*56) |
| 8 | machine weight | kg | 36 |
| 9 | time alarm | s | 999 |
| 10 | noise | db | Less than 50 |
Measuring particle size is a very important parameter in granular material engineering. Common methods for measuring particle size include:
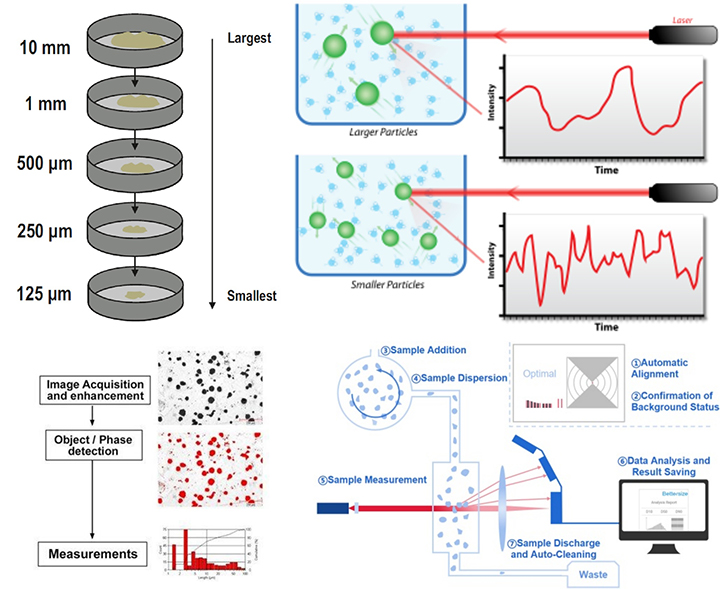
1、Sieve analysis: Separating particles by size by vibrating sieves on a set of standard sieves. The particle size distribution of the particles can be determined based on how the particles pass through screens with different apertures. It is mainly used to measure particles with a particle size greater than 38 μm, such as soil, sand, etc.
2、Laser particle size analysis: Use a laser particle size instrument to determine the particle size distribution of particles by measuring the scattering of laser light by the particles. This method is suitable for measuring the particle size of smaller particles. It has a wide measurement range and can measure particles from nanometer to millimeter scale.
3、Microscopic observation method: By observing the shape and size of particles through a microscope, the size of the particles can be estimated. This method is suitable for larger particles or when analysis of particle morphology is required. Mainly used to measure irregularly shaped particles.
4、Sedimentation method: By settling particles in a liquid medium, the particle size distribution of the particles is inferred based on the sedimentation speed of the particles. This method is suitable for the determination of fine particles. Mainly used to measure particles with a particle size between 0.1-150μm.
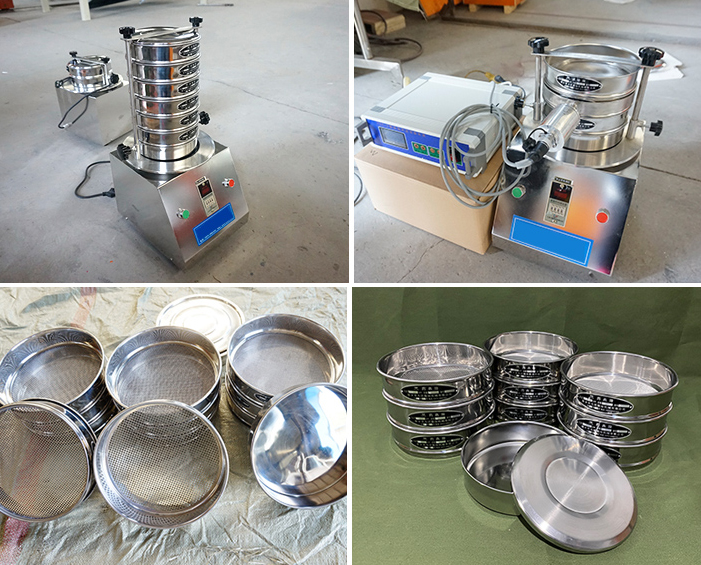

Sieves are an essential part of the sieve testing process. A test sieve is used to conduct particle screening tests. It is usually a small test sieve that can be used alone or placed on a screening machine to quickly and efficiently measure the size of solid particles from 125 mm to 20 microns.
A sieve is a tool used for particle screening, usually made of metal or plastic, that is designed to contain a medium consisting of openings of a specific size. Particles are separated into different particle size classes by the size of the sieve openings. Braided Wire vs. Side-by-Side Electroformed Wire The media can be braided wire mesh, perforated sheet, or electroformed wire mesh.
Test sieves are usually used in laboratories to conduct sieving tests on granular materials to evaluate the particle size distribution of granular materials. Suitable for particle size analysis and screening tests on small batches of granular materials, usually for research and experimental purposes.
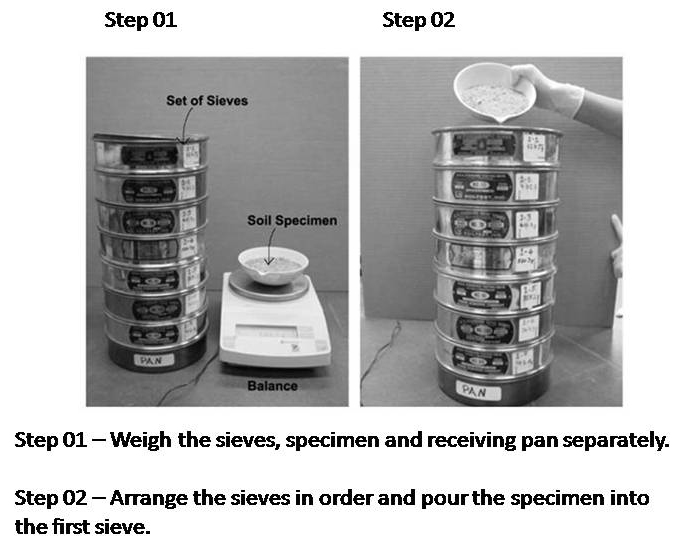

1. Take soil from air-dried loose soil samples by quartering. The quantity of soil is carried out according to the following figure in the table.
2. The sample was screened by 2mm, and the soil quality on and under the screen was respectively weighed out. Pour the soil on the 2mm screen into the upper layer of the coarse screen stacked in turn, and pour the soil under the 2mm screen into the upper layer of the fine screen stacked in turn (analysis screen from top to bottom aperture large to small stack). The sieve shaker is used to fully sieve out until the soil particle diameter on each sieve is greater than the mesh pore diameter, generally shaking the sieve for 15~30min;
3. Starting from large aperture sieve, each sieve will be removed in sequence, and the soil left on each sieve will be weighed respectively, accurate to 0.1g. The difference between the sum of the soil mass on each screen and the total soil mass shall not be greater than l% of the total soil mass.
4. Calculate the content of grain group and cumulative content, draw the gradation curve, get the characteristic particle size, analyze the gradation of soil, and name it according to the specification.
| Soil particle size (mm) |
<2mm | <10mm | <20mm | <40mm | >40mm |
| Sampling mass (g) |
100-300g | 300-900g | 1000-2000g | 2000-4000g | Above 4000g |
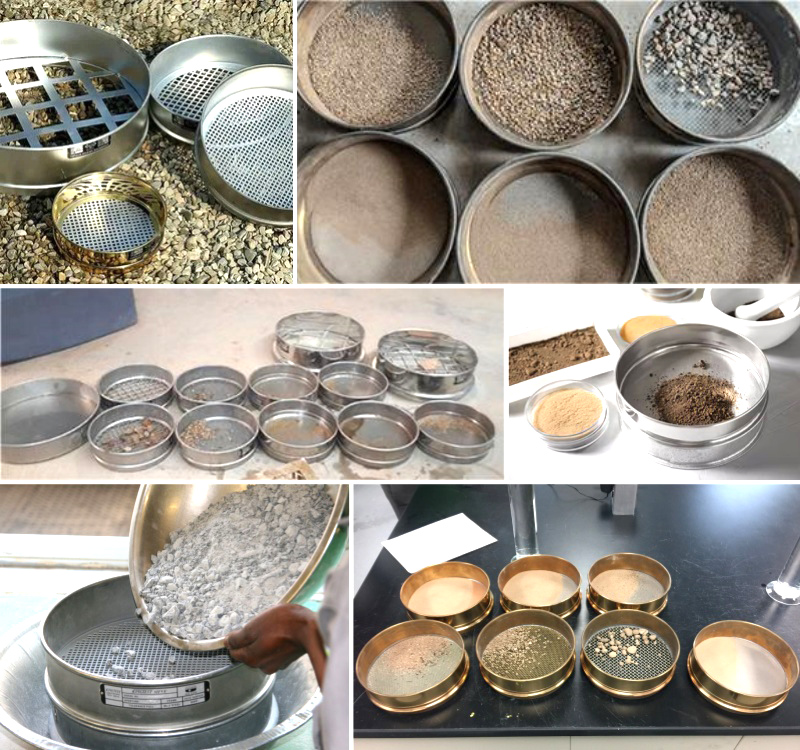
Preparation: Mix the sample to be tested evenly and weigh a certain amount of sample.
Sieving: Spread the sample evenly on the top sieve.
Sieving: Place the sieve frame on the sieving machine, start the sieving machine, and make the sieve vibrate up and down.
Weighing: After the sieving is completed, weigh the mass of the sieve and the undersize on each sieve.
Calculation: Calculate the particle content of different particle size ranges based on the mass of the sieve and the undersize.

Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.