









Used to measure the percentage of impurities in grain samples or the percentage of bran in rice, it is an inspection instrument to judge the quality of samples
![]()
![]()
Price:$20.00-$3,680.00/Set/Set
Consult now and enjoy a 10% discount
Sieve diameter: 75mm, 100mm, 200mm, 300mm, 400mm
Measuring range: 20µm-125mm
Feeding amount: 200g
Screen frame layers: 1-8 layers
Frame material:Brass,stainless steel,alumium,galvanized,pvc coated,etc.
Power: 0.125KW Noise: ≤50dB
Dimensions: 360*300*736 Weight: 36 kg
Application: For screening and particle size testing of various grains, wheat, barley, rye, oats, durum wheat, corn, sesame, beans, sesame, rice, millet and flour.
Commitment:
A grain sieve is a sieve commonly used in agriculture to analyze and grade grain according to particle size to ensure that the grain meets specific size and quality specifications, by analyzing the particle size distribution of grain, farmers and manufacturers can ensure their Products perform as expected in a variety of applications including baking, brewing and animal feed. Grain sieves are usually made of metal, such as brass or stainless steel, and consist of a circular frame and a mesh screen with a specific hole size and distribution. Grain sieves are available in a variety of sizes and mesh sizes, with common sizes ranging from #4 to #200. The exact size of the sieve used will depend on the particles being analyzed and the desired size range.

When using a grain sieve, place a grain sample on top of the sieve, then shake or stir the sieve to separate the grains by particle size. Smaller particles pass through the holes in the screen and collect on a tray or container below the screen, while larger particles remain on top of the screen.
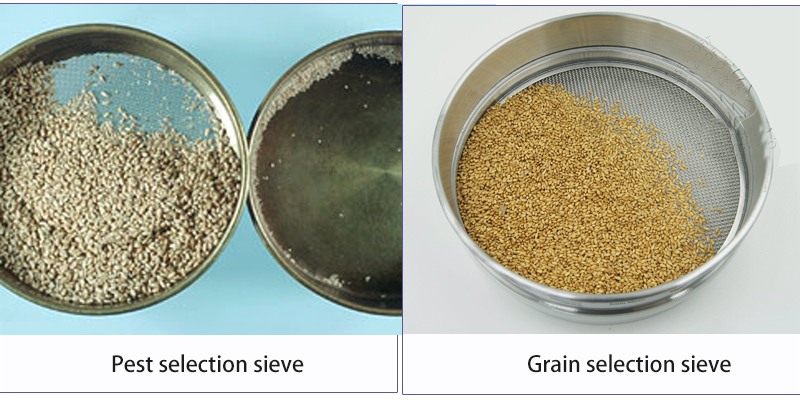


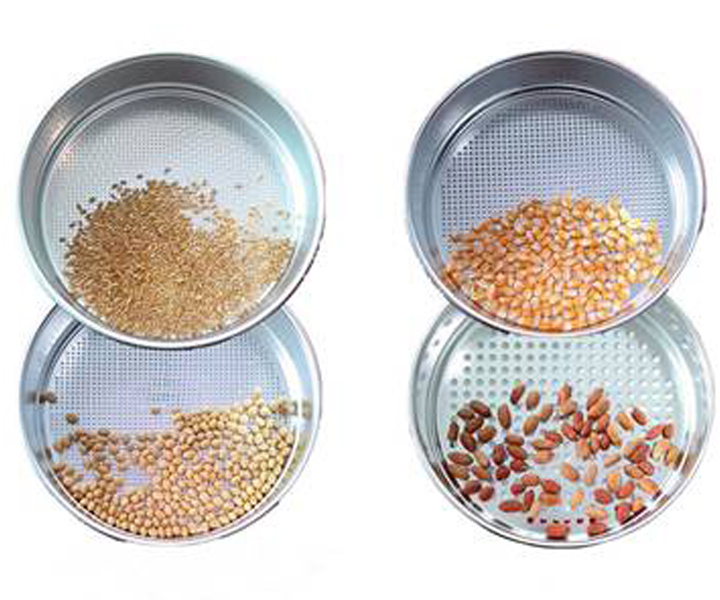
Grain sieves is a kind of testing instrument for checking the impurity content in grains, oil samples and the content of bran powder in rice to determine its quality grade. According to its different applications, it is divided into the following two types:
1. Pest selection sieve: The standard grain sieve is a special instrument for testing the degree of pest infestation in grains and oil samples, and determining the density of pests and the level of pests.
2. Grain selection sieve: an inspection instrument for inspecting the quality of grains such as wheat and corn to determine their quality grades.
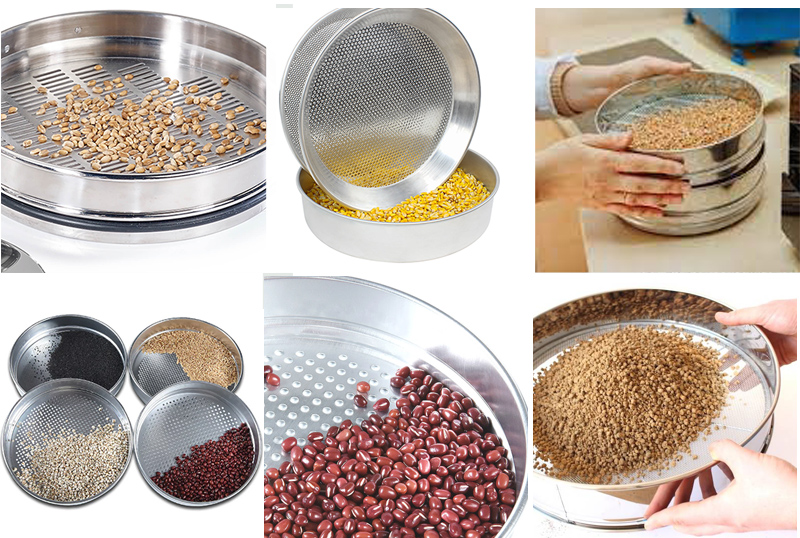

Grain sieves are widely used in various applications in the agricultural industry. Here are some common applications for grain sieves:
Quality Control: Used to ensure that grain meets specific size and quality specifications. By analyzing the particle size distribution of grains, farmers and manufacturers can ensure their products will perform as expected in a variety of applications including baking, brewing and animal feed.
Sorting and Grading: For sorting and grading grain according to particle size. This process helps ensure that similar sized grains are grouped together, making it easier to process and distribute the grains.
Research and Development: Used in research and development to study the physical properties of grains and their behavior under different conditions. This information can be used to develop new cereal products or improve existing cereal products.
Seed Testing: Used for seed testing to determine the purity and germination rate of grain seeds. This information is used to ensure that the seeds are high quality and produce healthy plants.
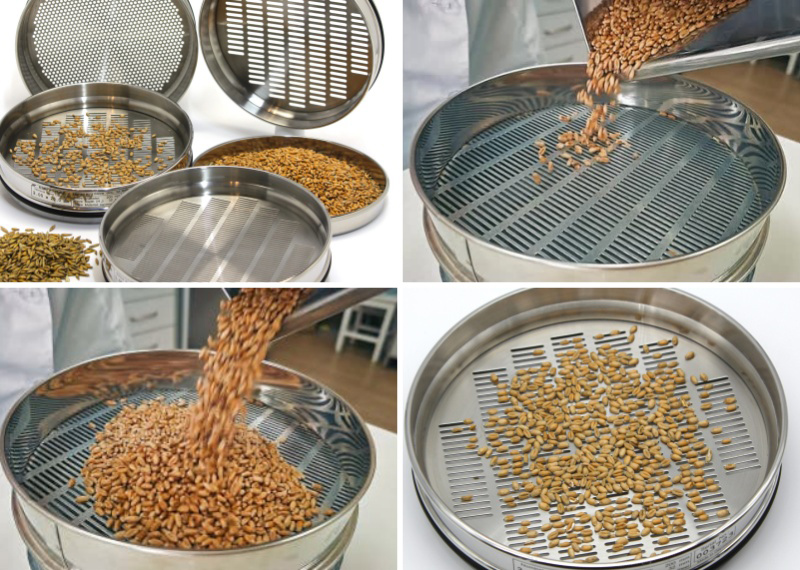
The sieving method of grain sieve is a process used to determine the particle size distribution of grain, sand, soil and other granular materials. The method involves passing a sample of material through a series of sieves with progressively smaller meshes and measuring the amount of material retained on each sieve.
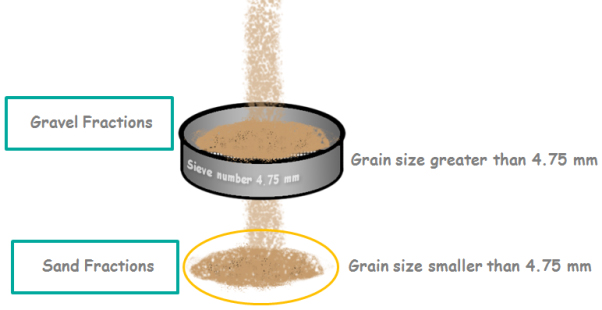
1. First collect and weigh a representative sample of the material.
2. Place the sample on the top sieve of the stack and shake the stack for the specified time using a mechanical or manual shaker.
3. Collect and weigh the material that passes through the top sieve and repeat the process for each subsequent sieve in the stack.
4. After all sieves have been processed, determine the amount of material retained on each sieve by subtracting the weight of material that passed through the sieves from the original weight of the sample.
5. Use these retained weights to calculate the particle size distribution of the material.
Grain sieves use a vibration device to vibrate the grain or granular materials in the screen box, so that the particles are separated on the screen. Smaller particles pass through the sieve apertures and fall into the container below, while larger particles are unable to pass through the sieve apertures and remain on the sieve. In this way, particles are classified according to size, impurities are removed, and particle sieving and separation are achieved. The frequency and amplitude of vibration can be adjusted to suit different particle sizes and sieving requirements.
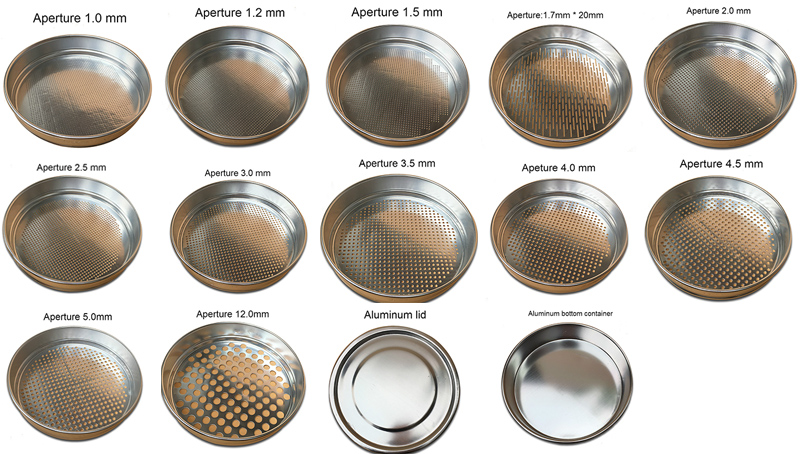

| No. | Technical | Technical indicate |
| 1 | Sieve Diameter | 200mm 8inch/300mm 12inch/100mm4inch/75mm 3inch |
| 2 | Material | Stainless steel or Brass |
| 3 | Inner height | 50mm and 60mm |
| 4 | Aperture size range | 0.02mm to 125mm |
| 5 | Hole model | Wire mesh and perforated plate |
| 6 | Detail aperture | 125, 106, 100, 90, 75, 63, 53, 50, 45, 37.5, 31.5, 25, 22.4, 19, 16, 13.2, 12.5, 11.2, 9.5, 8, 6.7, 6.3, 5.6, 4.75, 4, 3.35, 2.8, 2.36, 2, 1.7, 1.4, 1.18, 1, 0.85, 0.71, 0.6, 0.5, 0.425, 0.355, 0.3, 0.25, 0.212, 0.18, 0.15, 0.125, 0.106, 0.09, 0.075, 0.063, 0.053, 0.045, 0.038mm etc. |
| 7 | Use | Grading Standard Testing Sieve Test Sieve for soil test sieve, aggregate sieve, concrete test sieve, cement test sieve, asphalt test sieve, wet sieve, wire mesh sieve, perforated sieve, astm sieve, en sieve |
| Sieve Frame Material | Stainless steel sieve |
| Screen Material | Plated mild steel |
| Sieve height | 200 x 50mm, 300mm x 75mm, 315mm x 75mm, 350mm x 75mm, 400mm x 65mm, 450mm x 110mm Half Height: 200 x 25mm, 300mm x 38mm |
| Aperture size (Round Hole) | 1mm - 125mm |
| Aperture size (Square Hole) | 4mm - 125mm |
| If you have special requirements, please click on the contact us below to provide you with professional and customized services. Contact Us | |
Accurate and precise particle size analysis
Provides an accurate and precise method for analyzing grain size distribution. This information is critical to ensuring that the die meets specific size and quality specifications and performs as intended in a variety of applications.
Versatility
Available in a variety of sizes and mesh counts, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in agriculture, including sorting, grading and seed testing.
Consistent results
Grain sieves are designed to provide consistent and reproducible results, ensuring reliable and accurate analysis of multiple samples.
Multi-layer sieve
Up to 8 layers of sieve frames (including receiving trays) can be stacked, which can accurately separate a granular material into 1-7 granular segments at the same time.
Cost-effectiveness
Grain sieving is a cost-effective method of analyzing grain size distribution compared to other methods such as laser diffraction or image analysis.
Durability
They are usually made of high-quality materials, such as brass or stainless steel, ensuring that they are durable. Reliable quality, light weight, small size, easy to place.
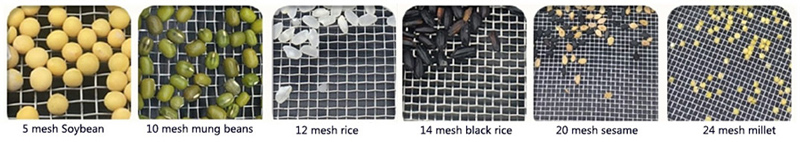
| No. | Type | Mesh(mm) | No. | Type | Mesh(mm) |
| 1 | 8# | 2.360 | 15 | 70# | 0.212 |
| 2 | 10# | 2.000 | 16 | 80# | 0.180 |
| 3 | 12# | 1.700 | 17 | 100# | 0.150 |
| 4 | 14# | 1.400 | 18 | 120# | 0.125 |
| 5 | 16# | 1.180 | 19 | 140# | 0.106 |
| 6 | 18# | 1.000 | 20 | 170# | 0.09 |
| 7 | 20# | 0.850 | 21 | 200# | 0.075 |
| 8 | 25# | 0.710 | 22 | 230# | 0.063 |
| 9 | 30# | 0.600 | 23 | 270# | 0.053 |
| 10 | 35# | 0.500 | 24 | 325# | 0.045 |
| 11 | 40# | 0.425 | 25 | 400# | 0.038 |
| 12 | 45# | 0.355 | 26 | 500# | 0.028 |
| 13 | 50# | 0.300 | 27 | >500# | <0.028 |
| 14 | 60# | 0.250 |

How and Screening Machine Helped Sand Industries
Here are some examples of customers who might use a grain sieves to test their grain:

Flour Mill
Flour mills produce flour from grains such as wheat, corn, and rice. Grain sieves are used in flour mills to remove impurities and to separate flour into different grades based on particle size.

Agricultural Research Institute
Agricultural research facilities can use grain sieves to study the physical properties of different types of grains and their suitability for various agricultural applications.

Seed Company
Seed companies produce and sell seeds for crops such as corn, soybeans, and wheat. Seed companies use grain sifters to test the quality and size of seeds before they are sold to farmers.

Food Processing Company
Food processing companies use grains such as wheat, corn and rice to produce a variety of foods. Grain sifters are used in these facilities to remove impurities and separate the grain into different grades based on particle size.
Here are some precautions to keep in mind when using a grain sieve:
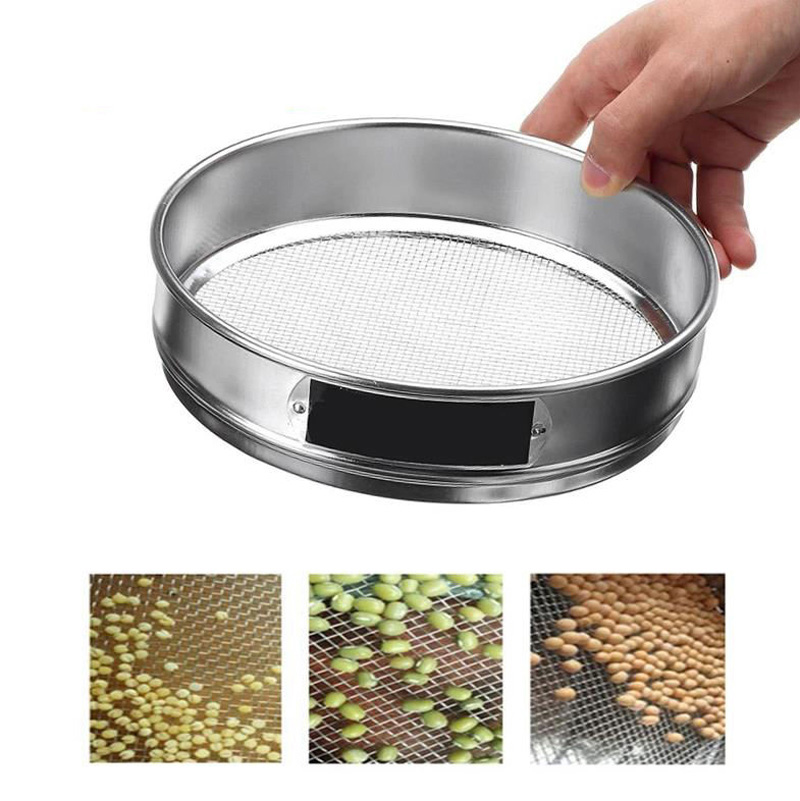

1. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling the material and the sieve stack.
2. Make sure the sieve stack is properly assembled and securely fastened before shaking. Check that the sieve frames and screens are clean and free from damage.
3. Use caution when shaking the sieve stack to avoid injury. If using a mechanical shaker, ensure that it is properly secured and follow any manufacturer instructions.
4. Use a representative sample of the material to ensure accurate results. Avoid using a sample that has been previously sifted or that is not fully mixed.
5. Take care when handling the material before and after sieving to prevent spills or contamination.
6. Clean the sieve stack after use to prevent cross-contamination and ensure accurate results for future tests.
7. Store the sieve stack in a dry location and protect it from damage to ensure its longevity and accuracy.
By taking these precautions, you can ensure accurate and safe results when using a grain sieve.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.