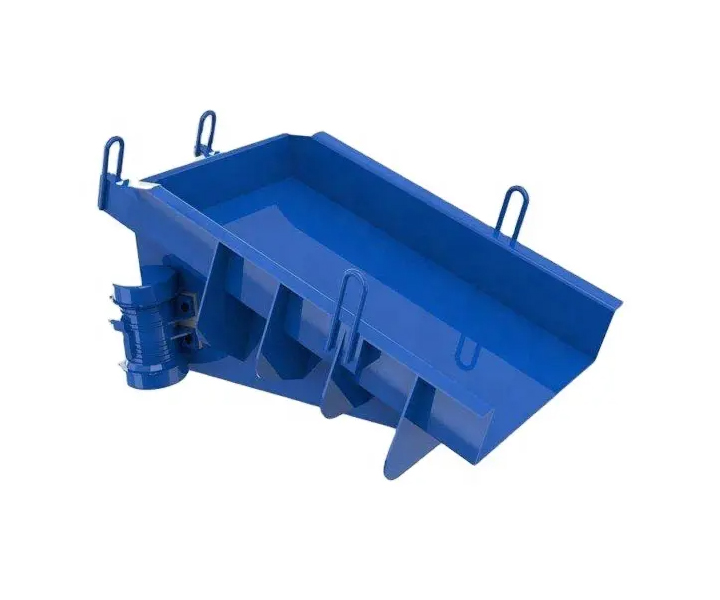
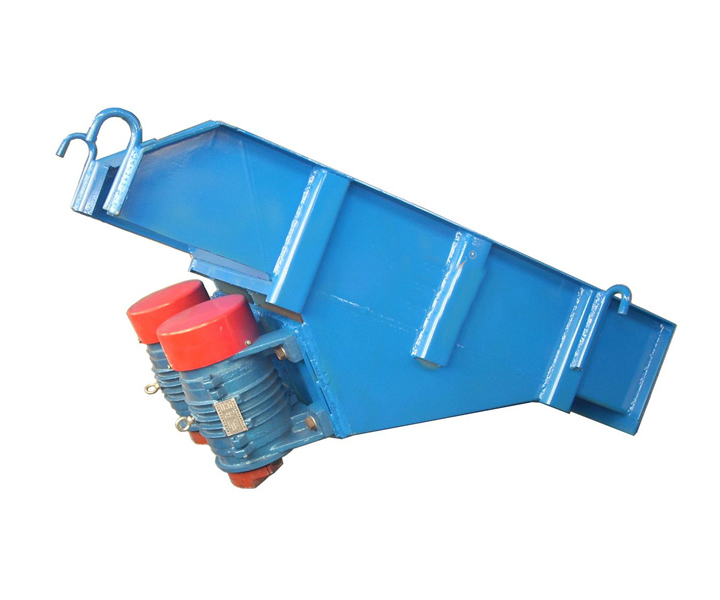
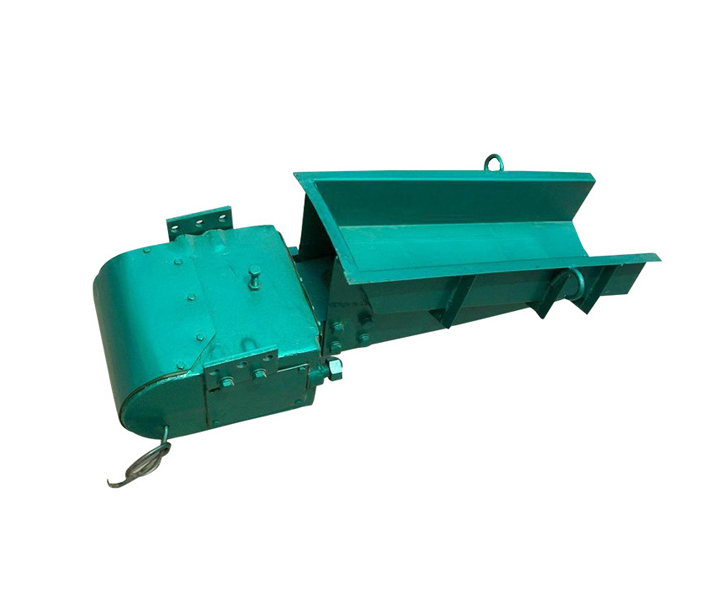
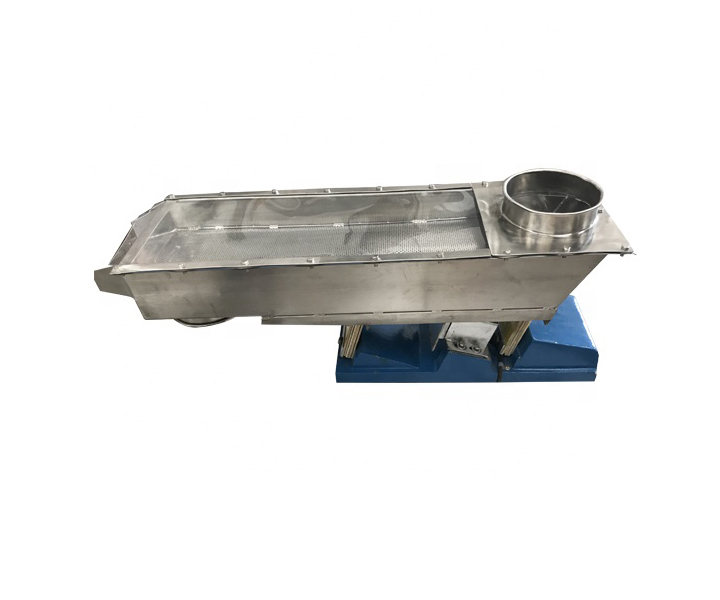










Consists of a trough or tube that vibrates and moves material in a controlled manner.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Price:$500.00 - $5,000.00/Set
Consult now and enjoy a 10% discount
Drive mode: motor/electromagnetic drive
Feeding particle size: 120~360mm
Output: 40~600 tons/hour
Frequency: 3000r/min
Material: carbon steel/stainless steel
Type: open/closed/hanging
Applications: Commonly used in a variety of industries including mining, construction, pharmaceuticals, food processing and recycling for handling bulk materials that are difficult to handle manually or that require precisely controlled feed rates
Commitment:Free Shipping/5 Days Delivery/30-Day Returns/Support Customization
Vibrating feeder, also known as a vibratory feeder or vibratory conveyor, is a device used to transport and feed bulk materials in a controlled manner. It utilizes vibrations to move materials along a trough or tube, ensuring a steady and controlled flow.

Vibrating feeders are widely used in various industries, including mining, construction, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and recycling. They are commonly used to feed bulk materials such as aggregates, ores, chemicals, powders, and granular materials.

Vibrating feeders offer several advantages, including precise and uniform material feeding, efficient material handling, and the ability to handle high-capacity loads. They are often used in conjunction with other equipment such as crushers, screens, and conveyors to form a complete material handling system.
| Types | Motor Type Vibrating Feeder | Electromagnetic Vibrating Feeder | Vibrating Tube Feeder |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Application | Combined with motor vibration and mechanical vibration, it is rugged enough to handle heavy-duty applications. | Typically used in applications requiring precise feeding of small or delicate materials. | Typically used to transport fragile or fragile materials that could be damaged or degraded by other types of feeders. |
| Features | Trough widths range from 6 inches to 5 feet and conveying lengths can be up to 10 meters. Multiple machines can be used in series to realize long-distance transportation. | Using electromagnetic drive to generate vibration, precise and highly controllable, adjustable feed rate. | Seals up to 20 feet (6 meters) and can be cascaded up to 100 feet (30 meters). |
| Working principle | The motor drives the eccentric block to rotate, generating vibration, causing the hopper or trough to vibrate, so that the material is thrown up and falls from the feeding port to achieve feeding. | The electromagnet generates periodic magnetic force to drive the armature to vibrate. The vibration force is transmitted to the trough through the spring, causing the material to move along the trough. | The vibration of the vibrating tube causes the material to fall from the tube port to achieve feeding. The vibrating tube is usually vibrated by the motor driving the eccentric block or electromagnet. |
Vibrating feeders are used in a wide variety of industries where controlled and reliable material transfer is required. Here are some common applications for vibratory feeders:

Mining and Quarrying: For transporting and feeding bulk materials such as ore, coal, aggregates and minerals. They are used in primary and secondary crushing systems, storage and recycling processes.
Construction and Aggregates: Used on construction sites and aggregate processing plants for efficient handling and supply of construction materials including crushed stone, gravel, sand and concrete. They ensure a continuous, uniform supply of material to crushers, screens and other processing equipment.
Recycling and Waste Management: Used in recycling plants and waste management facilities to process and supply a variety of recyclable materials and waste. They help to separate and sort different types of materials such as paper, plastic, metal and glass, thereby increasing the efficiency of the recycling process.
Food Processing: For precise control of the feeding of ingredients, additives and raw materials. They are used in applications such as ingredient, mixing, packaging and delivery of food, ensuring accurate dosing and preventing product contamination.
Pharmaceutical and Chemical: For precise feeding of granules, powders and other bulk materials. They are commonly used in processes such as mixing, sieving and packaging of pharmaceuticals, chemicals and ingredients.
Foundries and Metal Fabrication: Foundries and metal fabrication plants use vibratory feeders to convey and feed raw materials such as castings, scrap metal, and metal powder. They help regulate material flow during casting, melting and forming.
Ceramic and glass industry: Vibrating feeders are used in ceramic and glass manufacturing to control the supply of raw materials such as powders and granules. They ensure consistent material flow during forming, molding and firing.
The main functions of the vibrating feeder are as follows:

Uniform feeding: It can evenly feed materials to crushers, screeners, conveyor belts and other equipment to ensure that subsequent processes can be carried out stably and efficiently. Uniform feeding can avoid equipment load fluctuations caused by uneven materials and increase the stability of equipment operation.
Continuous conveying: The vibrating feeder can realize continuous material conveying, avoiding low production efficiency and equipment idleness caused by intermittent feeding. Continuous conveying can ensure continuous operation of the production line and improve overall production efficiency.
Screening function: During the conveying process, the vibrating feeder can simply screen the material, remove fine particles or impurities, and ensure the quality of the material in the subsequent process.
Prevent blockage: The vibration of the vibrating feeder can prevent the material from being blocked during the conveying process, especially for sticky or wet materials, vibration can effectively prevent the material from adhering to the trough.
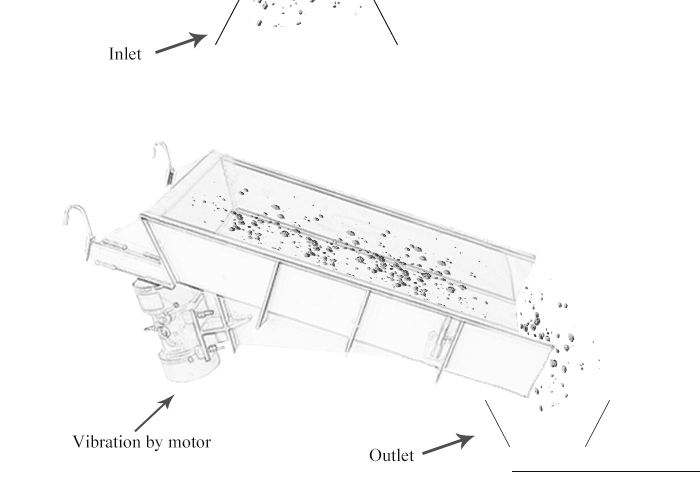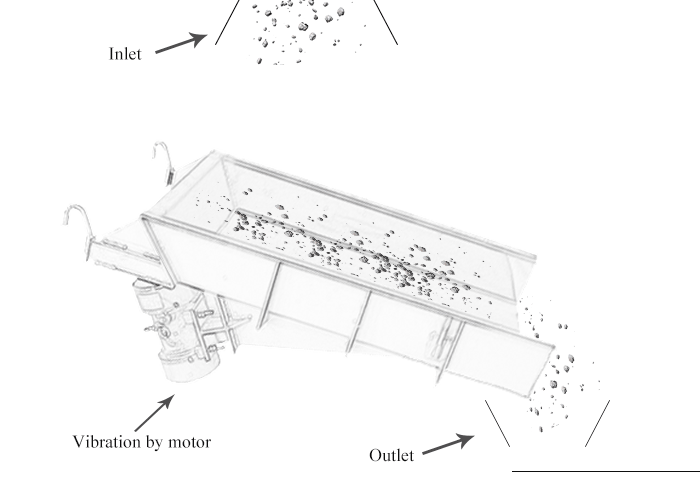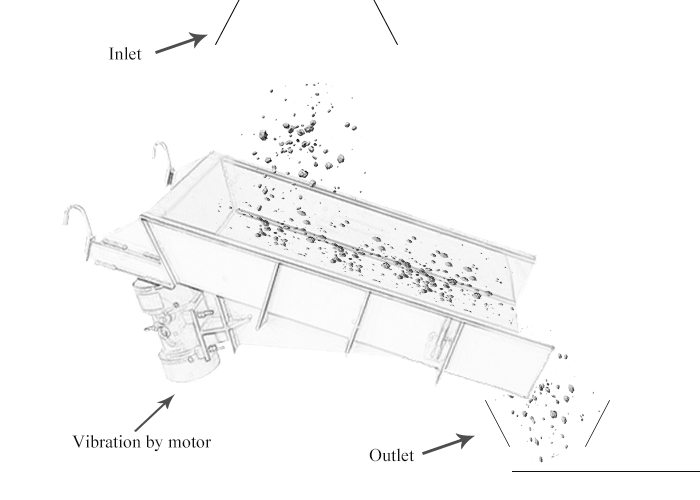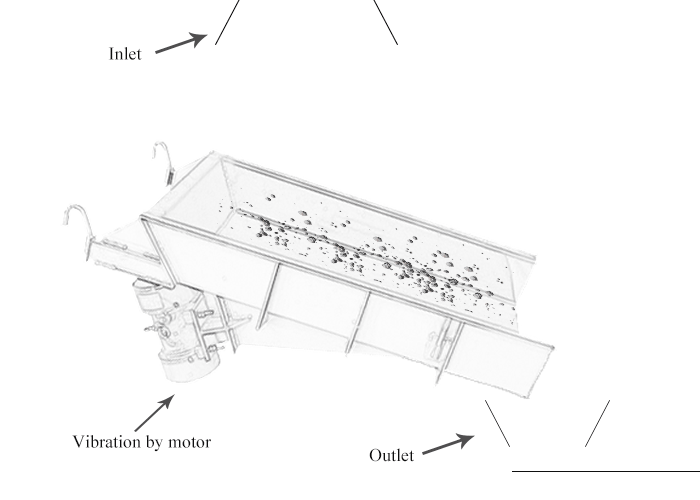
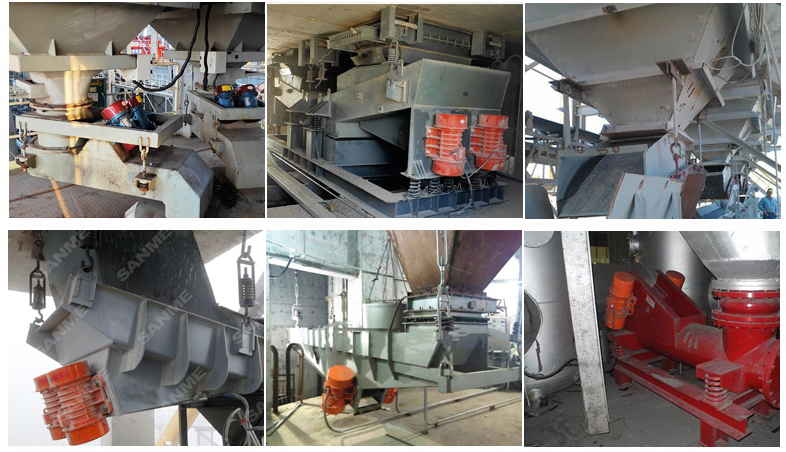
The feeding process of the vibrating feeder is realized by using a special vibrating motor or two motors to drive the vibrator to drive the feeding trough to vibrate periodically and linearly along the inclined direction. The material in the material is thrown up and jumps forward according to the trajectory of the parabola. The throwing and falling are completed in an instant. Due to the continuous excitation of the excitation source, the feeding trough vibrates continuously, and the coal in the trough jumps forward continuously, so that the achieve the purpose of feeding.
Precise, uniform feeding
Bulk materials can be fed precisely and evenly. Controlled vibration ensures consistent material flow, prevents maldistribution and minimizes segregation. This is especially important in processes that require precise dosing or mixing of materials.
Efficient material handling
Very efficient in handling bulk materials. Vibration facilitates material flow, reduces friction and allows for smoother movement. This efficiency increases productivity and reduces energy consumption.
Adjustable feed rate
Offers adjustable feed rates, allowing the operator to control the flow of material according to process requirements. The feed rate can be easily adjusted by modifying the vibration intensity or frequency, allowing flexible handling of different materials and optimizing the production process.
Noise reduction and dust removal
Vibrating feeders produce minimal noise compared to other types of feeders, making them suitable for environments where noise control is important. Additionally, the controlled material flow and enclosed design of some vibratory feeders can help reduce dust emissions and promote a cleaner, safer workplace.
Easy to maintain
They are designed for reliable operation and require minimal maintenance. Routine maintenance tasks may include lubrication, inspection, and occasional component replacement.
Equipment protection
By controlling flow and ensuring consistent feed, vibratory feeders prevent material buildup or blockage in hoppers, chutes or crushers that can cause equipment damage or downtime.
Motor Type Vibrating Feeder for Plastic Particles
Electromagnetic Vibrating Feeder for Salt
| Model | Productivity (t/h) | Feed chute size (W*L*Hmm) |
Operation mode | Feed particle size (mm) |
Vibration motor | Weight (Kg) |
||||
| Voltage (V) |
Frequency (Hz) |
Model | Power (KW) |
Vibration frequency (times/min) |
||||||
| GZG30-4 | 15 | 300*1000*160 | Continuous | 120 | 380 | 50 | YZD2.5-4 | 0.18*2 | 1450 | 110 |
| GZG40-4 | 30 | 400*1200*160 | YZD5-4 | 0.25*2 | 155 | |||||
| GZG50-4 | 50 | 500*1200*160 | YZD8-4 | 0.4*2 | 190 | |||||
| GZG60-4 | 80 | 600*1800*180 | 180 | YZD16-4 | 0.75*2 | 410 | ||||
| GZG70-4 | 100 | 700*1800*200 | 180 | TZP20-4 | 1.1*2 | 440 | ||||
| GZG80-4 | 200 | 800*2000*225 | 200 | TZD32-4 | 1.5*2 | 640 | ||||
| GZG90-4 | 300 | 900*1500*300 | 250 | YZD50-4 | 2.2*2 | 730 | ||||
| GZG110-4 | 400 | 1100*1500*300 | 900 | |||||||
| GZG130-4 | 500 | 1300*1500*400 | 350 | 1000 | ||||||
| GZG70-6 | 80 | 700*1800*200 | 150 | YZD20-6 | 1.5*2 | 960 | 440 | |||
| GZG80-6 | 160 | 800*2000*225 | 180 | YZD30-6 | 2.2*2 | 670 | ||||
| GZG90-6 | 240 | 900*1500*300 | 240 | YZD40-6 | 3.0*2 | 740 | ||||
| GZG110-6 | 320 | 1100*1500*300 | YZD50-6 | 3.7*2 | > 940 | |||||
| GZG130-6 | 400 | 1300*1500*400 | 320 | 1040 | ||||||
| GZG150-6 | 500 | 1500*1800*500 | 2000 | |||||||
| GZG180-6 | 800 | 1800*1800*500 | YZD75-6 | 5.5*2 | 2590 | |||||
| ZG200-6 | 1000 | 2000*2000*500 | 360 | 3700 | ||||||
The basic components of a vibrating feeder include:
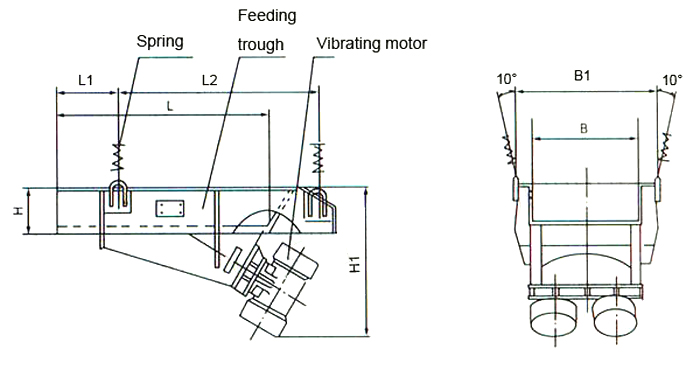
Vibrating Base or Electromagnetic Drive: This is the power source that generates the vibrations. It can be an electric motor with an eccentric weight mounted on it or an electromagnetic drive that creates a magnetic field to produce vibrations.
Feeder Trough or Tube: The feeder trough or tube is a trough-shaped or tube-shaped structure that holds and transports the bulk materials. It is typically made of durable materials such as steel or stainless steel. The trough is designed to accommodate the desired volume and flow rate of the materials being conveyed.
Vibrating Mechanism: The vibrating base or electromagnetic drive transmits vibrations to the feeder trough or tube. These vibrations cause the materials to move along the trough or tube in a controlled manner. The amplitude and frequency of the vibrations can be adjusted to control the flow rate and ensure smooth material movement.
Control Unit: A control unit is used to regulate the vibrations and adjust the flow rate of the materials. It allows operators to set the desired parameters such as vibration intensity, frequency, and feed rate.

A mining company introduced a vibrating feeder produced by Xinxiang Dahan Factory for uniform feeding before ore crushing. The equipment runs stably, significantly improving the crushing efficiency and production line stability.
Another building materials company uses vibrating feeders for raw material transportation in cement production, solving the problem of material blockage and ensuring production continuity and product quality.
In addition, a chemical company uses vibrating feeders to accurately feed powdered chemical raw materials, realizing automated production, improving production efficiency and reducing manual operation errors.
These successful cases demonstrate the wide application and remarkable effects of vibrating feeders in different industrial fields.

1. Determination of output: The output of GZG vibrating feeder is given by river sand as the standard material (bulk specific gravity is 1.6T/m3). When the bulk specific gravity of the material is greater than 1.6T/m3, the output can be selected according to the rated value; when the bulk specific gravity of the material is 1.2-1.6T/m3, the output can reach 0.9-1.0 times the rated output. When the specific gravity of the material pile is 0.8-1.2T/m3, its output can reach 0.8-0.9 times of the rated value. When the specific gravity of the material pile is less than 1.6T/m3, the thickness of the material layer must be appropriately increased to increase the output.
For materials that are difficult to be conveyed by the vibrating feeder (such as talc, titanium dioxide, white mud, flour, clay, etc.), as well as hydrophilic materials with large water content, the output should be determined according to the test. If necessary, the tank body should be properly inclined and installed (generally inclined downward by 10 to 15 degrees) to increase the feeding amount.
2. Selection of control box: The matching control box of this series of feeders is a reverse-connected brake control box, which can make the feeder stop quickly when it stops, so that the feeder can quickly pass through the resonance area and avoid excessive vibration. damage to the machine. The control box has the functions of overcurrent, overvoltage, and phase failure protection. In addition, functions such as energy consumption braking, fast and slow feeding, remote control and stepless speed regulation can be added according to process requirements. Please specify when ordering.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.