Sieve analysis is a common laboratory testing method used to measure the particle size distribution of granular materials. Through sieve analysis, the content percentage and distribution of particles of different particle sizes can be determined, providing important information for engineering design and material evaluation. The method of sieve analysis and its operating steps in the laboratory will be introduced in detail below.
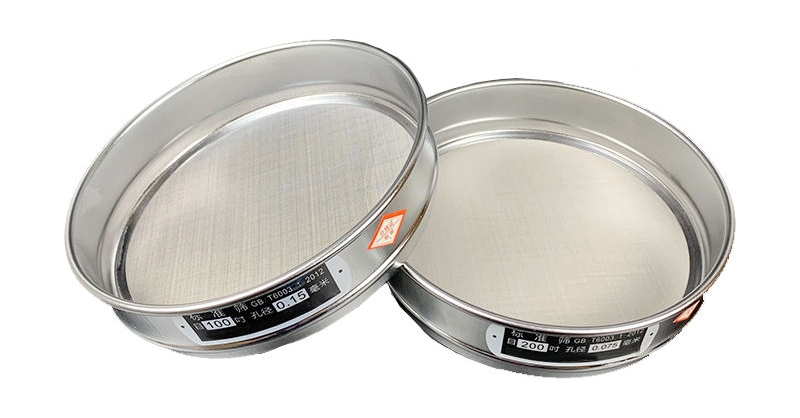

The method of sieve analysis is based on the physical force between particles and uses the pore size of the sieve to separate particles according to particle size. Larger particles cannot pass through a screen with a smaller pore size, while smaller particles can pass through a screen with a larger pore size. Through a series of screens with different apertures, granular materials can be classified according to particle size to obtain a particle size distribution curve.
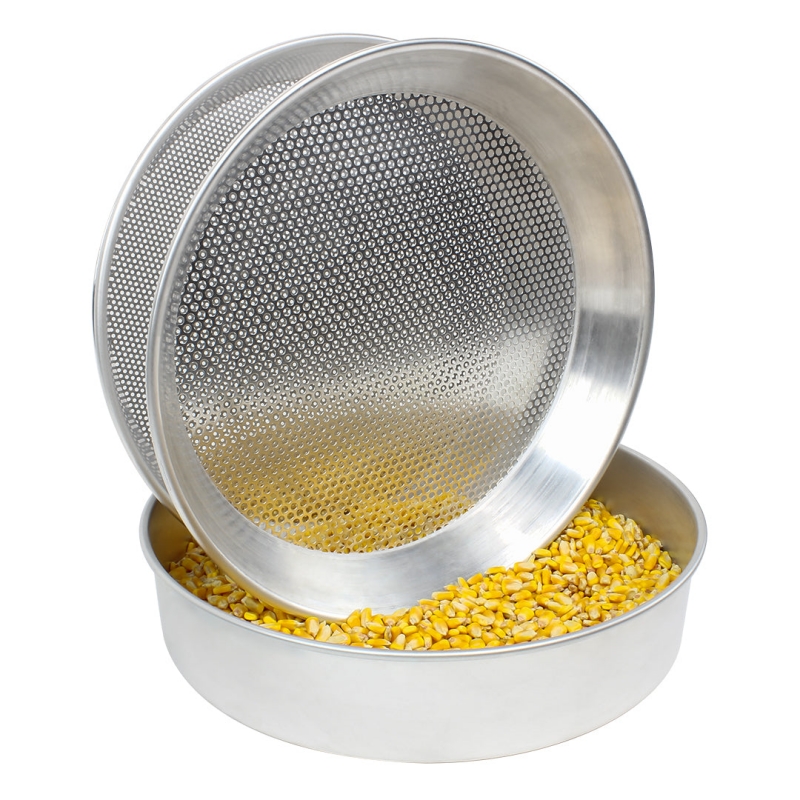

1. Prepare samples: Obtain representative samples from the field or laboratory, and perform necessary sample processing, such as removing impurities and organic matter. Ensure sample quality and representativeness.
2. Prepare the screening device: Select the appropriate screen combination and install the screen on the screening device. Make sure there are no holes and gaps between the screens.
3. Weigh the sample: According to the test requirements, weigh a sample of a certain mass and record the mass. The quality of the sample should be determined based on the test requirements and material properties.
4. Sieve: Pour the weighed sample into the screening device, cover the device, and start the vibration device for screening. The screening time can be adjusted as needed.
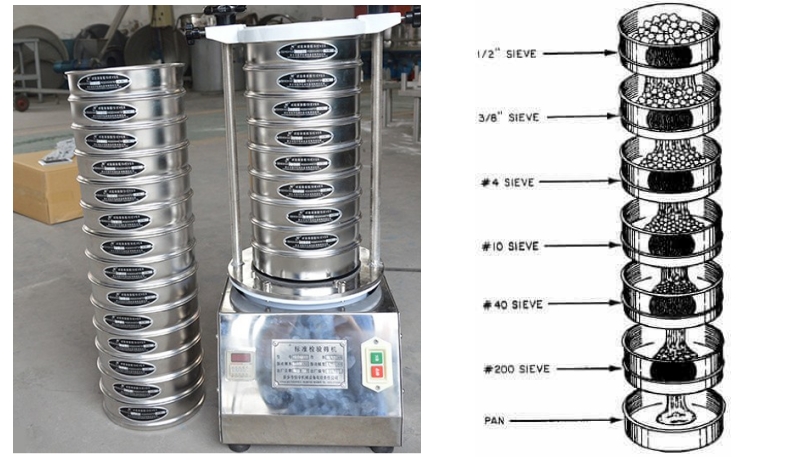
5. Weigh the screened particles: After screening, collect the particles on each screen and weigh them. Record the particle mass on each screen.
6. Calculate particle distribution: Based on the particle mass on each screen, calculate the percentage content and cumulative percentage content of particles. Draw a particle distribution curve to reflect the particle size composition and distribution of the material.
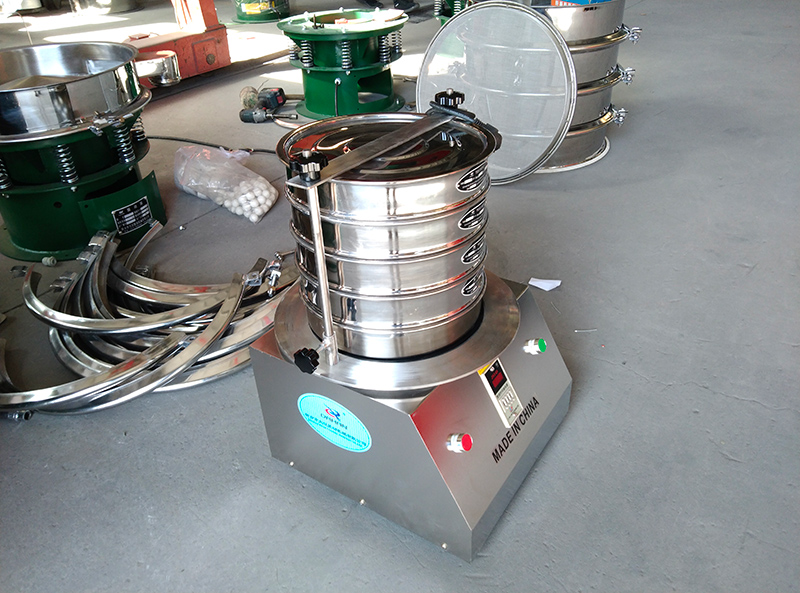
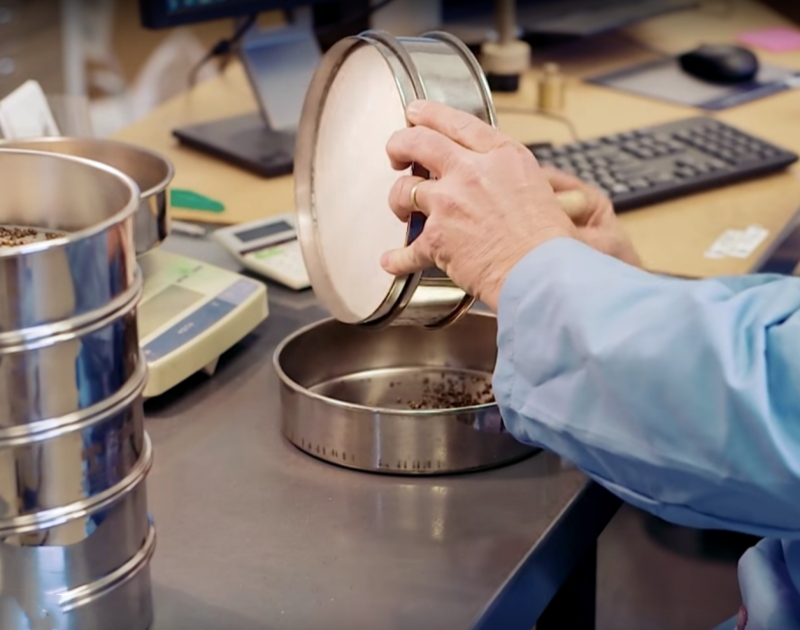


1. Screen selection: Select the appropriate screen combination according to the characteristics of the sample and the test requirements. The pore size of the screen should be such that it meets the desired particle size classification range.
2. Screening time: The selection of screening time should take into account the characteristics of the sample and the test requirements. Typically, larger particles are screened out faster, while smaller particles require longer screening times.
3. Sample processing: During sample processing, care should be taken to avoid particle breakage and agglomeration to maintain the original characteristics of the sample.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.