Soil sieve machine is a sieve used to filter soil. It is widely used in various laboratories for sample grading, sieving, analysis, and testing. It basically belongs to the category of sieves, and its main function is to sieve soil. Soil sieves are usually used with fully automatic laboratory vibrating screens to improve efficiency and safety. This tool is very useful in laboratory environments and can help researchers to conduct detailed analysis and processing of soil samples.

The use of soil sieve machine is not limited to laboratory environments. In fact, soil sieve machine, as a vibrating screen for screening soil, is also one of the technical equipment for soil treatment. Soil sieve machine can screen out impurities such as stones, gravel, and rotten leaves in the soil, and grade the soil to screen out fine soil with smaller particle size. Soil sieve machine has many types such as linear vibrating screen and circular vibrating screen, which are suitable for different processing needs, such as automated processing in assembly line operations.
| Mesh size comparison table | |||||
| Number of stitches | granularity μm | Number of stitches | granularity μm | Number of stitches | granularity μm |
| 5 Order | 3900 | 140 | 104 | 1300 | 11 |
| 10 | 2000 | 170 | 89 | 1600 | 10 |
| 16 | 1190 | 200 | 74 | 1800 | 8 |
| 20 | 840 | 230 | 61 | 2000 | 6.5 |
| 25 | 710 | 270 | 53 | 2500 | 5.5 |
| 30 | 590 | 325 | 44 | 3000 | 5 |
| 35 | 500 | 400 | 37 | 3500 | 4.5 |
| 40 | 420 | 425 | 33 | 4000 | 3.4 |
| 45 | 350 | 460 | 30 | 5000 | 2.7 |
| 50 | 297 | 540 | 26 | 6000 | 2.5 |
| 60 | 250 | 650 | 21 | 7000 | 1.25 |
| 80 | 178 | 800 | 19 | ||
| 100 | 150 | 900 | 15 | ||
| 120 | 124 | 1100 | 13 | ||
| Millimeter and mesh comparison table | |||||
| Millimeters/mm | Screen size/mm | Number of stitches | Millimeters/mm | Screen size/mm | Number of stitches |
| Φ200*50mm | 4.75 | 4 | Φ200*50mm | 0.250 | 60 |
| 4.00 | 5 | 0.212 | 70 | ||
| 3.35 | 6 | 0.180 | 80 | ||
| 2.80 | 7 | 0.150 | 100 | ||
| 2.36 | 8 | 0.125 | 120 | ||
| 2.00 | 10 | 0.106 | 140 | ||
| 1.70 | 12 | 0.090 | 170 | ||
| 1.40 | 14 | 0.0750 | 200 | ||
| 1.18 | 16 | 0.0630 | 230 | ||
| 1.00 | 18 | 0.0530 | 270 | ||
| 0.850 | 20 | 0.0450 | 325 | ||
| 0.710 | 25 | ||||
| 0.600 | 30 | ||||
| 0.500 | 35 | ||||
| 0.425 | 40 | ||||
| 0.355 | 45 | ||||
| 0.300 | 50 | ||||
| Powder fineness particle size unit conversion comparison table | |||
| Particle size(m) | Micrometerμm | nanometernm | Mesh unit (mesh) |
| 10-4m | 100μm | 100000nm | 180 (mesh) |
| 10-5m | 10μm | 10000nm | 1800 (mesh) |
| 10-6m | 1μm | 1000nm | 1.8Many mesh |
| 10-7m | 0.1μm | 100nm | 18Many mesh |
| 10-8m | 0.01μm | 10nm | 180Many mesh |
| 10-9m | 0.001μm | 1nm | 1800Many mesh |
| 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm); | |||

Soil sieve machine selection is a common soil particle analysis method used to determine the content and distribution of different particle sizes in the soil. Soil screening is usually carried out using sieves of different apertures. The screening process classifies soil particles according to size, providing important data for the study of soil physical properties and engineering design.
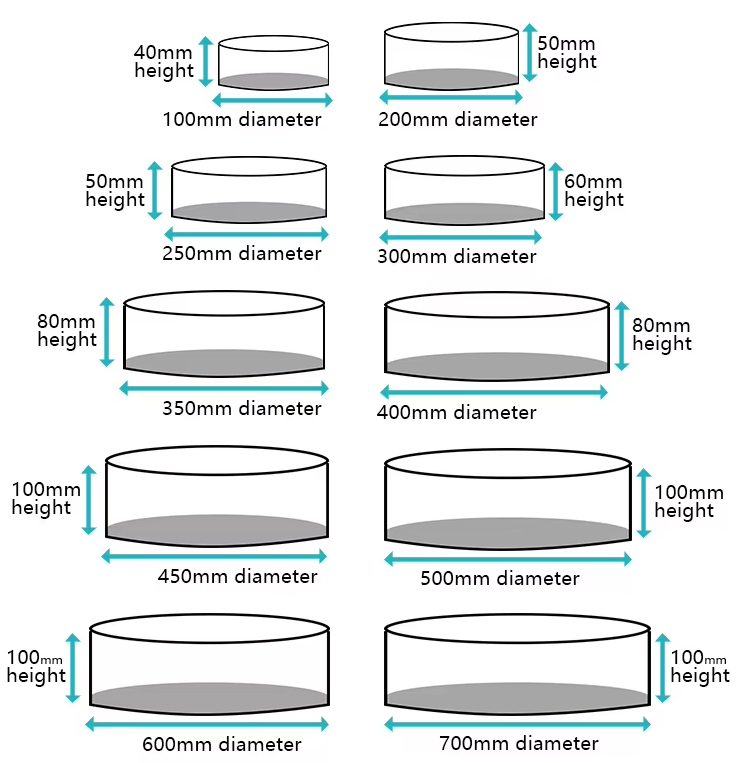
Prepare soil samples: First, soil samples need to be collected from the field or laboratory and pre-processed such as drying and crushing for subsequent screening analysis.
Choose the right sieve: The sieve aperture used is determined according to the needs. Usually a series of sieves with different apertures are selected to screen the soil sample multiple times to obtain particles of different particle size ranges.
Sieving process: Pour the pre-treated soil sample into the sieve, and then gently shake or vibrate the sieve to separate the soil particles according to size through the sieve aperture. Larger particles will be retained on the upper sieve, and smaller particles will fall through the sieve into the container below.
Weighing and recording: After the screening is completed, the soil particles remaining on each sieve are weighed, and the weight of the particles in each sieve is recorded for subsequent data processing and analysis.

Data processing and analysis: According to the weight data of the particles in each sieve, the particle content in different particle size ranges can be calculated, and a particle size distribution curve or table can be drawn to analyze the particle composition of the soil.

Particle analysis test is also an important part of soil analysis, which is used to determine the percentage of each particle group in the total mass of soil particles. When the particles larger than 0.074mm in the particle analysis test exceed 15% of the total mass of the sample, the sieving method will be used for determination. For particles that cannot be screened, the density meter method or pipette method is used to determine the relative content of each particle group. Finally, the particle size distribution curve is drawn for soil classification. This process also reflects the application and importance of soil screening in soil analysis.
Address:China,Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road.